Odoo Implementation Guide 2025: Avoid $250K+ Failures
by Aria Shaw
The Truth About Odoo Implementation (And Why Most Fail)
If you’re researching Odoo implementation for your business, you’ve discovered that what should be straightforward software deployment has transformed into an overwhelming maze of decisions, vendors, and technical jargon.
You’ve wasted months in “discovery meetings” with consultants who babble in jargon but can’t deliver a straight answer about timeline or budget.
You’re drowning in conflicting advice about Odoo Community vs Enterprise, watching your project timeline dissolve while your team grows frustrated with the current system.
This chaos affects most businesses.
Last week, a manufacturing CEO revealed how their company incinerated $250,000 on a failed Odoo implementation—eighteen months of delays, three different consulting firms, and a system that collapsed handling basic inventory tracking.
Another business owner uncovered their “99% complete” implementation missing critical integrations that would drain another $75,000 to fix.
Nobody tells you upfront: Odoo implementation isn’t about the software—it’s about transformation management disguised as a technology project.
The vendors market it like installing an app, but you’re rewiring your entire business nervous system.
One wrong assumption about data migration, one overlooked workflow requirement, or one untested integration can obliterate months of work and tens of thousands of dollars.
The Promise vs Reality Gap:
Odoo’s promise seduces: an all-in-one business management platform that’ll streamline everything from sales to accounting to inventory.
Most implementations either crash outright or limp along as expensive, frustrating compromises that solve yesterday’s problems while creating tomorrow’s headaches.
When teams execute Odoo implementation correctly, Odoo revolutionizes businesses.
Research proves that properly implemented Odoo systems empower companies to slash operational overhead by 40% within six months.
They cut month-end closing time from two weeks to three days (imagine getting your financial reports while they’re still relevant).
They achieve real-time visibility into business operations instead of relying on outdated spreadsheet reports from last month.
Success and failure separate based on wielding a proven, step-by-step process that anticipates every pitfall before you fall into it.
Don’t worry. This guide will walk you through the entire Odoo implementation process, step by step, like a set of Lego instructions.
By the time you finish reading, you’ll master exactly how to plan and execute your Odoo implementation from start to finish. You’ll discover how to manage external consultants effectively (without getting taken for a ride), recognize the red flags that trigger project disaster before they destroy your timeline and budget, and optimize your system for long-term success rather than just getting to go-live.
📋 Download: Comprehensive Implementation Checklist - Complete phase-by-phase checklist to track your progress throughout the entire implementation journey
Phase 1: Strategic Decision & Business Case
What Is Odoo Implementation Process and Why It Matters
Most guides won’t reveal: Odoo implementation isn’t about installing software—it’s about orchestrating a complete business transformation while your company continues operating.
When that photography business owner upgraded to Odoo 18 and described it as “nothing short of a nightmare,” with their entire website format destroyed and months of design work undone, they learned this lesson the hard way. A version upgrade explodes into a business-critical project that can make or break your operations.
The Real Definition of Odoo Implementation: Odoo implementation weaves Odoo’s modular ERP system into your existing business operations while simultaneously redesigning your workflows, migrating your data, training your team, and maintaining business continuity. This combines technology project, change management initiative, and strategic business transformation.
This matters because analysts predict the global ERP market will reach $78.4 billion by 2026, and over 7 million businesses are betting their operations on platforms like Odoo. The sobering reality shows 23% of ERP implementations succeed, while the average cost overrun is 189%.
Why 2025 Is Different: The stakes reach new heights, but so do the opportunities. Odoo 18’s AI-driven automation and enhanced integration capabilities mean that implementations can deliver 40% productivity improvements and reduce operational overhead by 35%. Failed implementations cost more and disrupt more than ever.
Building Your Odoo Implementation Business Case
The companies that succeed with Odoo implementation spend more time on their business case than on technical planning. The data-driven approach that works:
Odoo Implementation Cost Breakdown 2025
Odoo Enterprise Pricing (Current 2025 Rates):
- Standard Rate: $24.90 per user per month (US pricing)
- European Rate: €19.90 per user per month (billed annually)
- No per-app fees: Whether you need CRM, Inventory, Project management, or all modules, the price stays the same
Total Implementation Investment: Analysis of 2025 implementation data shows these budget amounts:
| Business Size | Users | Total Investment | Software (Annual) | Implementation | Training/Customization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Business | 5-15 | $5,000 - $15,000 | $1,800 - $5,400 | $3,000 - $8,000 | $1,000 - $2,000 |
| Medium Business | 25-50 | $15,000 - $50,000 | $7,500 - $15,000 | $8,000 - $25,000 | $3,000 - $15,000 |
| Enterprise | 50+ | $50,000+ | $15,000+ | $25,000 - $100,000+ | $15,000+ |
ROI Analysis: Why Odoo Beats the Competition
Independent analyses prove Odoo’s five-year total cost of ownership (TCO) costs 40-60% less than SAP and Microsoft Dynamics. In real numbers:
Example: 25-User Manufacturing Company
- Odoo Total 5-Year Cost: ~$75,000
- SAP Business One 5-Year Cost: ~$125,000
- NetSuite 5-Year Cost: ~$150,000
Operational improvements that compound over time deliver the real ROI.
Companies using Odoo see a 30% increase in sales productivity thanks to AI-driven lead scoring, a 40% reduction in implementation time compared to traditional ERP systems, a 25% improvement in inventory turnover because they know what they own and where it sits, and a 50% reduction in month-end closing time that lets finance teams focus on analysis instead of data collection.
The Photography Business Reality Check: Remember that photographer who faced the Odoo 18 upgrade disaster? Their annual Odoo cost ran under $300. Compare that to the thousands they would have lost from the months of downtime if they couldn’t recover. Doing Odoo implementation wrong costs more than doing it right.
Building Your Internal Business Case
The presentation framework that gets executive buy-in every time:
Slide 1: The Pain Point “Our current system costs us [X hours/week] in manual processes and prevents us from [specific business goal].”
Slide 2: The Opportunity “Odoo implementation will reduce our operational costs by [X%] and enable [specific business capability].”
Slide 3: The Investment “Total investment: $[X] over [Y] months. Payback period: [Z] months based on [specific savings/revenue increase].”
Slide 4: The Risk Mitigation “We’ve identified [X] implementation risks and have specific mitigation strategies for each.”
Odoo Enterprise vs Community Implementation Comparison
This decision alone can make or break your implementation. Choose based on documented case studies, not marketing materials.
Odoo Community vs Enterprise: The 2025 Reality
Odoo Community looks free on paper, but free software doesn’t exist—software where you pay in different ways. It works for startups, small businesses under 10 users, or companies with strong technical teams who manage their own infrastructure. The hidden costs include self-hosting (which runs $35-100 per month), ongoing maintenance, security updates, and backup management. You’ll miss out on mobile apps, Studio (the visual app builder that proves essential), advanced reporting, and multi-company consolidation.
Odoo Enterprise costs $24.90 per user per month, which seems expensive until you factor in everything you get. It’s perfect for growing businesses, companies that need support when things break, and teams without technical expertise who want software that works. You get all the Community features plus mobile access, Studio, advanced modules, and support that responds. For 15 users, you’re looking at $4,482 annually—less than most companies spend on coffee.
Decision Framework: Community vs Enterprise
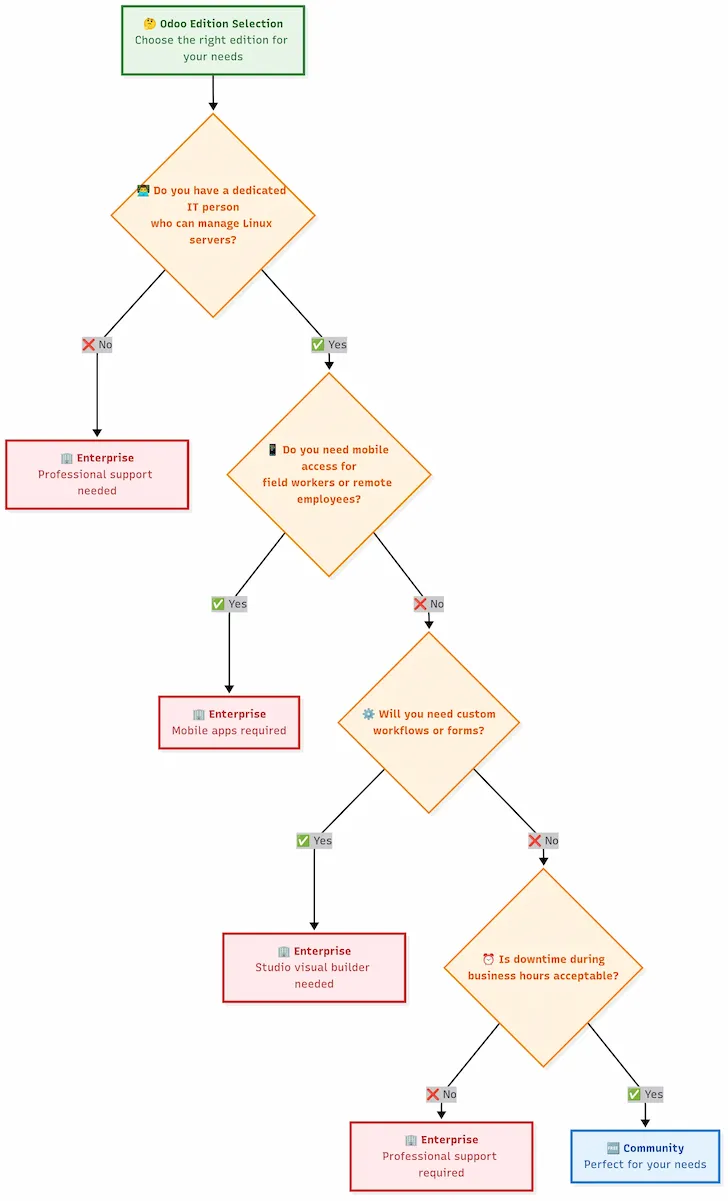 Decision tree to help you choose between Odoo Community and Enterprise editions based on your technical capabilities and business requirements
Decision tree to help you choose between Odoo Community and Enterprise editions based on your technical capabilities and business requirements
🎯 Before you finalize your hosting budget: Odoo Enterprise costs $24.90/user/month, but your total hosting expenses depend heavily on your deployment model choice. Self-hosting might save $300/month on Odoo.sh fees but costs $800/month in staff time and infrastructure. Our free Hosting Advisor analyzes your budget, team capacity, and risk tolerance to show you which option has the lowest true total cost for your situation—including hidden costs most calculators miss. Get your personalized recommendation (2 min) →
Cloud vs On-Premise: The 2025 Strategic Choice
The market shifts toward cloud-first deployments:
| Factor | Cloud Deployment | On-Premise |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Recommendation | Recommended for 90% of businesses | Only for specific requirements |
| Implementation Timeline | 2-4 weeks | 3-6 months |
| Upfront Investment | No server hardware or IT infrastructure | High capital investment required |
| Updates & Maintenance | Automatic updates and security patches | Manual management required |
| Scalability | Add users instantly | Hardware planning required |
| Data Control | Managed by provider | Full data sovereignty |
| Custom Integrations | Standard integrations available | Deep ERP integration with legacy systems |
| Optimal User Volume | Ideal for <100 users | 100+ concurrent users with heavy customization |
| Primary Use Case | Most small to medium businesses | Highly regulated industries, complex legacy systems |
Key Decision Factors:
- Cloud Advantages: Faster deployment, lower costs, automatic maintenance, instant scaling
- On-Premise Advantages: Complete data control, deep customization, enterprise-scale performance
Total Cost Comparison (5-Year Analysis):
| Business Size | Cloud Deployment | On-Premise | Cost Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small (10 users) | $15,000 - $25,000 | $35,000 - $50,000 | 40-50% savings |
| Medium (25 users) | $35,000 - $60,000 | $75,000 - $120,000 | 50-60% savings |
| Large (50+ users) | $70,000 - $120,000 | $150,000 - $300,000 | 55-65% savings |
Note: On-premise costs include server hardware, IT infrastructure, maintenance, security, and backup systems
Competitive Analysis: Why Odoo Over Alternatives
Analysis across the ERP spectrum provides comparison data. A comparison based on 2025 realities:
| Comparison Factor | Odoo | SAP Business One | NetSuite | Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Timeline | 4-12 weeks | 6-18 months | 4-8 months | 6-12 months |
| 5-Year Cost (25 users) | ~$75,000 | ~$125,000 | ~$150,000 | ~$110,000 |
| Pricing Model | Flat $24.90/user | Per-user + modules | $99/user + add-ons | Per-user + app licenses |
| Customization | Visual Studio builder | Technical consultants | Limited flexibility | Complex licensing |
| User Experience | Modern, consistent | Traditional interface | Web-based | Mixed interfaces |
| Mobile Access | Included in Enterprise | Additional cost | Additional modules | Varies by module |
| Integration | Built-in between modules | Third-party required | Oracle ecosystem | Additional licenses |
| Open Source Foundation | Yes - unlimited flexibility | No | No | No |
| Best For | SME to mid-market | Large enterprises | Oracle ecosystem | Microsoft-centric orgs |
Winner Analysis
| Category | Winner | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Odoo | 40-60% lower total cost of ownership |
| Speed to Market | Odoo | Fastest implementation timeline |
| Flexibility | Odoo | Open source foundation enables unlimited customization |
| User Experience | Odoo | Modern, intuitive interface with consistent design |
| All-in-One Value | Odoo | All modules included in flat pricing |
When NOT to Choose Odoo
Be honest about these scenarios. If you need deep industry modules like healthcare practice management or legal case management, specialized solutions serve you better than trying to force Odoo into workflows that don’t match its design. If you’re Fortune 500 with thousands of users and complex compliance requirements, SAP or Oracle might justify their price tags. And if your business runs on legacy systems that resist replacement, and integration would be more expensive than your current pain, the devil you know is better than the angel you don’t.
Odoo Implementation Timeline and Success Rate Planning
The uncomfortable truth: most implementation timelines represent fantasy. Here are realistic expectations based on project data.
Realistic Implementation Timelines (2025)
Simple Implementation (5-15 users, standard modules):
- Planning & Setup: 2-3 weeks
- Data Migration: 1-2 weeks
- Testing & Training: 2-3 weeks
- Total: 6-8 weeks
Medium Implementation (15-50 users, some customization):
- Planning & Discovery: 3-4 weeks
- Configuration & Customization: 4-6 weeks
- Data Migration & Testing: 3-4 weeks
- Training & Go-Live: 2-3 weeks
- Total: 12-17 weeks
Complex Implementation (50+ users, heavy customization):
- Planning & Architecture: 6-8 weeks
- Development & Configuration: 8-12 weeks
- Integration & Migration: 4-6 weeks
- Testing & User Acceptance: 4-6 weeks
- Total: 22-32 weeks
The Success Rate Reality Check
While Odoo claims a 95% implementation success rate, industry data tells a different story:
- Industry experts consider only 23% of all ERP implementations “successful”
- 50-75% of ERP projects fail on their first attempt
- Projects exceed budgets by an average of 189%
Four factors separate success from failure.
Executive commitment makes the biggest difference—projects with active CEO or owner involvement achieve 85% success rates because teams align when leadership pays attention.
Realistic timeline planning is crucial; projects that plan for 150% of estimated time rarely exceed budget because they build in buffer for reality.
Change management isn’t optional—companies that invest in user training see 40% higher adoption rates because people use systems they understand.
Partner selection can make or break everything; working with certified Odoo partners increases success rates by 60% because experience matters.
Planning for Success: The 90-Day Rule
This framework works: Plan your implementation in 90-day phases, regardless of project length.
Phase 1 (Days 1-90): Foundation is where you build the bedrock. You’ll analyze business requirements (what you need versus what you think you want), form your team and get them trained on the basics, configure core modules to match your workflows, and start cleaning up your data. Don’t skip the data cleanup—garbage in, garbage out isn’t just a saying, it’s a prophecy.
Phase 2 (Days 91-180): Implementation is where the rubber meets the road. You’ll migrate your data (hopefully clean by now), set up core workflows that people will use, provide initial user training before they forget everything, and run pilot testing with a small group brave enough to be guinea pigs.
Phase 3 (Days 181-270): Optimization is where you go from “it works” to “it works well.” Full rollout to everyone, advanced feature implementation for power users, process refinement based on what you learned during pilot testing, and performance optimization because nobody likes slow software.
This approach lets you course-correct quickly and prevents the “18-month death march” that kills ERP projects.
Red Flags to Watch For
Before we move to technical planning, these warning signs show your Odoo implementation is headed for disaster.
If your vendor promises everything is “standard” without asking detailed questions about your business processes, they don’t understand your needs—they’re just trying to close the deal.
Any timeline shorter than 8 weeks for anything but the simplest setup is fantasy; quality implementation takes time, and anyone promising faster is cutting corners you’ll pay for later.
If there’s no discussion of change management or user training, run—technical implementation is only half the project, and the human half is usually harder.
Fixed-price proposals without discovery should make you suspicious; how can they quote accurately without understanding your requirements?
And if they pressure you to customize rather than adapt processes, remember that it’s often cheaper to change your process than to change the software.
In the next phase, we’ll dive into the technical foundation and architecture planning that turns your business case into a working system. But first, you need to nail down these strategic decisions. Every successful Odoo implementation I’ve seen started with a rock-solid business case and realistic expectations.
Phase 2: Technical Foundation & Architecture Planning
Odoo Implementation Hardware Requirements and Planning
Most Odoo implementations collapse here.
You’ve made your strategic decisions, but now you need to translate those into technical specifications.
“It works” versus “it works reliably at scale” separates based on building your infrastructure foundation right from day one.
Remember that photography business owner whose Odoo 18 upgrade became a nightmare?
Part of their problem was inadequate infrastructure planning. When you don’t size your servers or plan your deployment architecture, routine updates explode into business-threatening events.
Odoo 18 System Requirements (2025 Updated)
The real-world requirements, not the marketing minimum specs:
Get personalized specifications: Our Odoo Requirements Calculator provides exact CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth recommendations based on your user count, module selection, and transaction volume—eliminating guesswork from infrastructure planning.
| Deployment Size | Users | CPU | RAM | Storage | Network | Additional Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | 5-15 | Dual-core minimum Quad-core recommended |
4GB minimum 8GB recommended |
20GB minimum SSD strongly recommended |
10Mbps dedicated internet per 5 concurrent users | Basic setup |
| Medium | 25-50 | Quad-core minimum 8-core recommended |
8GB minimum 16GB recommended |
50GB minimum SSD required |
25Mbps+ dedicated internet | Separate PostgreSQL server recommended |
| Large | 100+ | 8+ cores for app server | 32GB RAM minimum for app server | 500GB+ with daily backup | 50Mbps+ dedicated internet | Dedicated database server: 16+ cores, 64GB RAM, NVMe SSD High-availability Nginx load balancer |
The PostgreSQL Reality Check: Odoo 18 ships with PostgreSQL 15 support, and your database configuration is critical. Production-proven configurations:
-- Essential PostgreSQL settings for Odoo
max_connections = 200
shared_buffers = 256MB
effective_cache_size = 1GB
work_mem = 4MB
maintenance_work_mem = 64MB
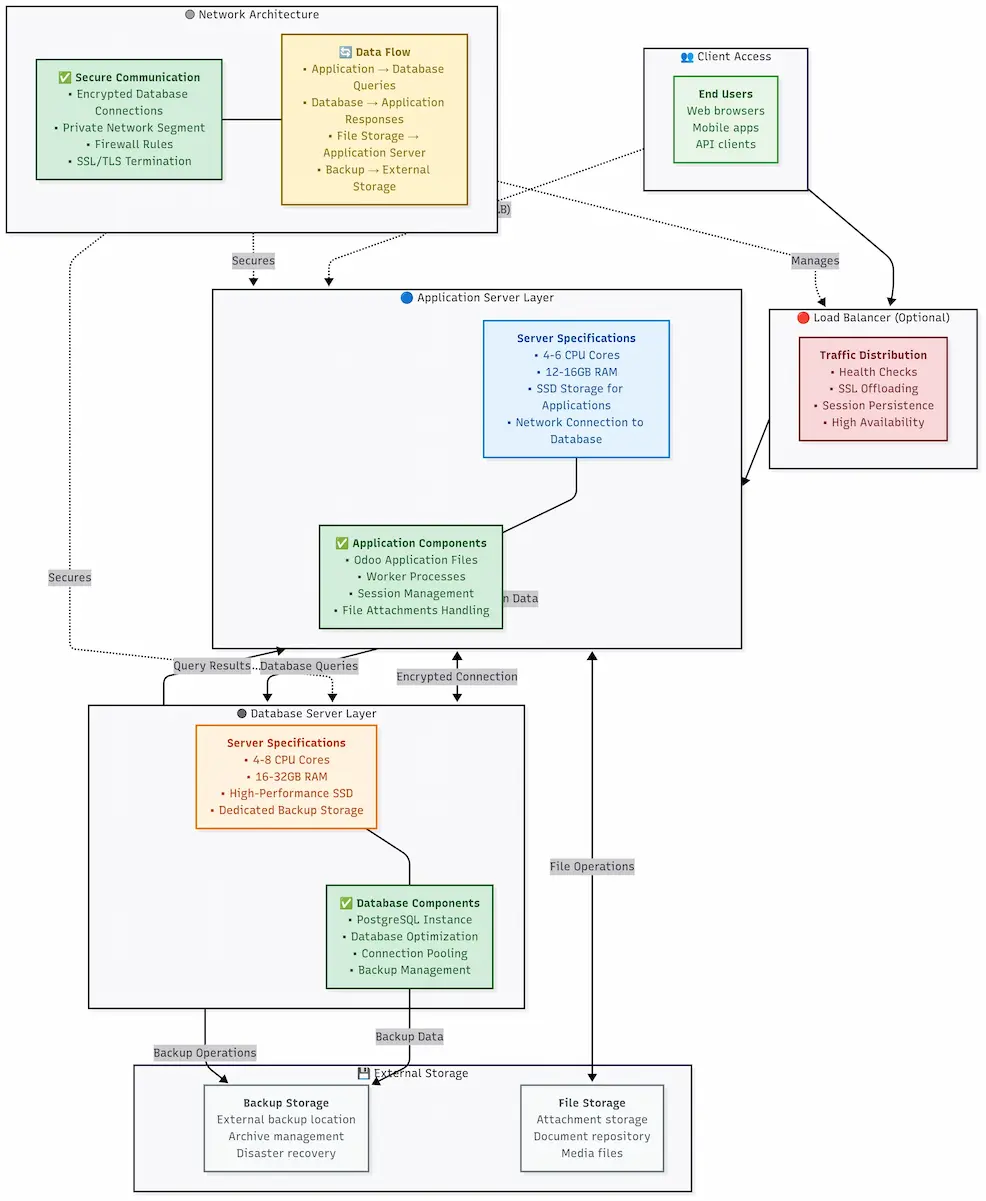 Enterprise-grade Odoo architecture with separated application and database layers for optimal performance and security
Enterprise-grade Odoo architecture with separated application and database layers for optimal performance and security
Operating System Recommendations
2025 deployment analysis shows the OS breakdown:
Linux (Recommended for 95% of installations):
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS: Best community support, easiest package management
- Ubuntu 24.04 LTS: Latest features, tested with Odoo 18
- CentOS Stream/Rocky Linux: Enterprise environments with strict compliance needs
Why Linux wins: The Odoo ecosystem runs on Linux. When things break (and they will), you’ll find solutions faster, get better community support, and have access to performance optimization tools that don’t exist on Windows.
Windows (Only if required): Organizations mandating Windows face:
- 15-20% performance penalty
- More complex backup and maintenance procedures
- Limited community support for troubleshooting
- Additional licensing costs
Enterprise Odoo Implementation Architecture Design
We distinguish the amateur implementations from the professional ones here.
Your architecture decisions determine whether your Odoo system can survive growth, integration challenges, and business changes three years from now.
Single-Server vs Multi-Server Architecture
Single-Server Setup (Up to 25 users): One machine hosts everything:
- Odoo application
- PostgreSQL database
- Nginx reverse proxy
- File storage
Pros: Simple, cost-effective, easy to backup Cons: Single point of failure, limited scalability
Multi-Server Architecture (25+ users): Professional Odoo implementations start here:
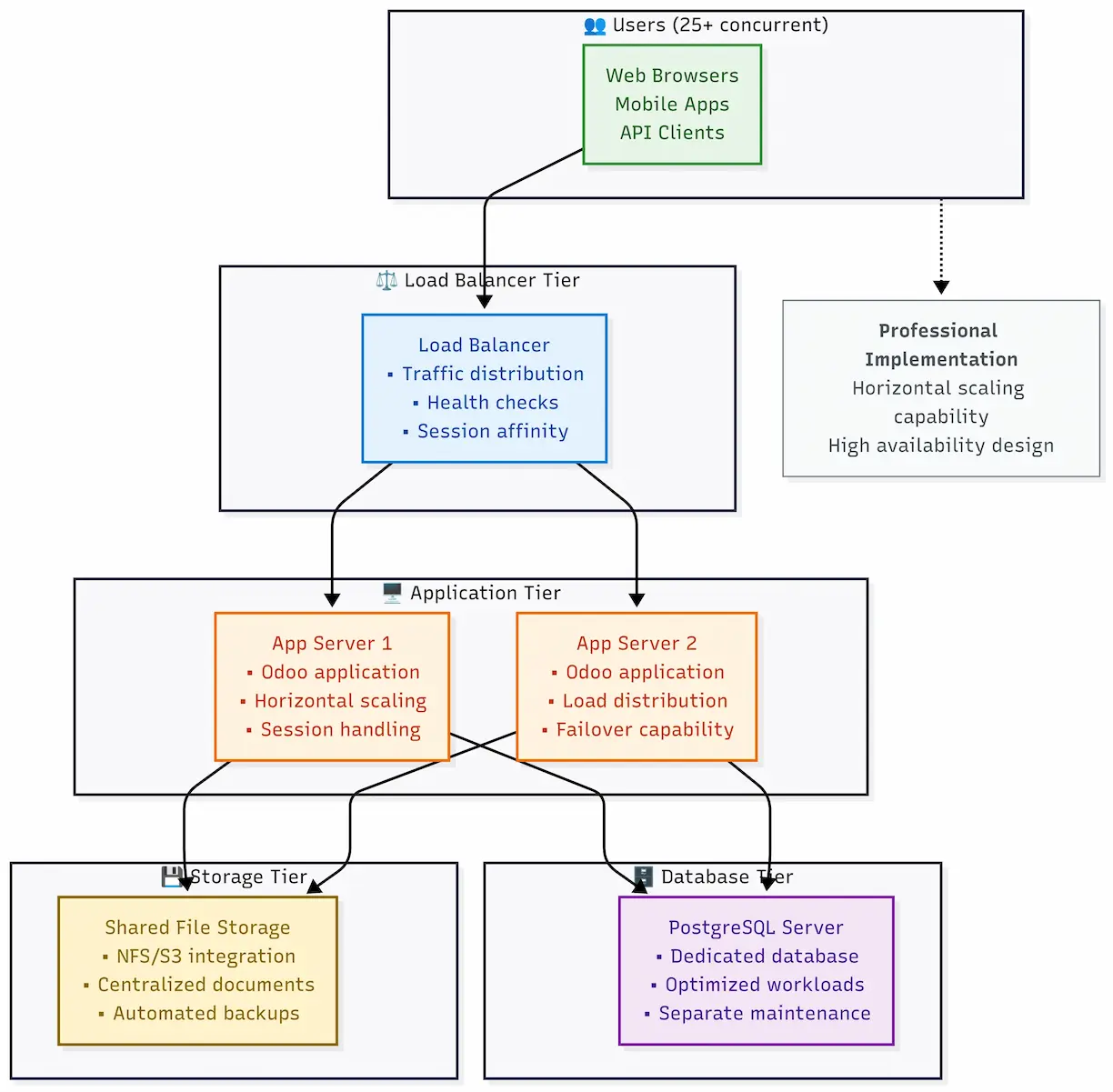 Professional multi-tier Odoo architecture with horizontal scaling capability and high availability design
Professional multi-tier Odoo architecture with horizontal scaling capability and high availability design
🤔 Overwhelmed by architecture choices?
Single-server, multi-server, cloud, on-premise, self-hosted, managed... You just read about PostgreSQL tuning, load balancers, and storage tiers. But here's the real question: Which model actually fits YOUR team's technical capacity and budget?
Our free Hosting Advisor cuts through the complexity. Answer 6 honest questions about your IT staffing, budget, and risk tolerance—get a vendor-neutral recommendation that shows you exactly which architecture has the lowest total cost of ownership for your specific situation. Used by 2,400+ businesses to make this critical decision.
Application Tier:
- Dedicated Odoo application servers
- Horizontal scaling capability
- Session affinity handling
Database Tier:
- Dedicated PostgreSQL server
- Optimized for database workloads
- Separate backup and maintenance cycles
Storage Tier:
- Shared file storage (NFS/S3)
- Centralized document management
- Automated backup systems
Multi-Company Setup Best Practices
If you’re planning multi-company operations, nail this right from the beginning.
Analysis proves implementations attempting to retrofit multi-company support cost more than implementing it upfront.
Planning Your Company Structure: Blueprint your company hierarchy before creating anything in Odoo:
- Parent Company: Your main legal entity
- Subsidiaries: Separate legal entities
- Branches: Same legal entity, different locations
- Cost Centers: Departments within the same entity
Critical Setup Sequence:
- Create parent company first (cannot convert later)
- Enable fiscal localization immediately (before any configuration)
- Build chart of accounts with company-specific prefixes
- Establish separate warehouses and locations
- Configure user access rights and company assignments
Data Sharing Strategy:
- Products: Share across companies unless legal requirements demand separation
- Customers: Share for group-wide customer management
- Vendors: Usually shared for better purchasing power
- Financial Data: Separate by company for compliance
Cloud vs On-Premise: The 2025 Strategic Choice
This decision impacts everything in your technical architecture.
Need help deciding? Our Odoo Hosting Advisor evaluates your technical capacity, budget constraints, and growth trajectory to recommend whether cloud (VPS/managed), on-premise, or Odoo.sh aligns with your business reality—preventing costly hosting mismatches.
Real-world comparison based on 2025 data:
Cloud Deployment Analysis
Total Cost Comparison (5-year, 25 users):
Cloud Deployment:
- Odoo Enterprise licenses: $37,485 (25 × $24.90 × 12 × 5)
- Hosting (professional): $6,000
- Implementation: $15,000
- Total: ~$58,500
On-Premise Deployment:
- Odoo Enterprise licenses: $37,485
- Hardware (servers, networking): $25,000
- IT staff overhead: $30,000 (15% of IT salary over 5 years)
- Implementation: $20,000
- Total: ~$112,500
Performance Reality Check:
- Cloud: 99.9% uptime SLA, managed updates, monitoring
- On-Premise: Depends on your IT capability
When Cloud Dominates (90% of businesses):
- Under 100 users
- Standard business processes
- Limited IT staff
- Growth-focused organization
- Multi-location operations
When On-Premise is Required:
- 200+ users with heavy customization
- Strict data sovereignty requirements
- Complex legacy system integrations
- Dedicated IT team with Linux expertise
Hybrid Architecture: The Best of Both Worlds
For organizations, consider a hybrid approach:
Core Odoo: Cloud-hosted for reliability and maintenance Custom Applications: On-premise for specific integrations Data Warehouse: On-premise for analytics and reporting File Storage: Cloud storage with on-premise backup
Odoo Implementation Security Considerations
Security isn’t an afterthought—it’s foundational architecture.
The companies that suffer breaches are the ones who thought they’d “add security later.”
SSL/TLS Configuration
Every production Odoo installation requires HTTPS. The 2025 approach:
SSL Certificate Options:
- Let’s Encrypt (Free, automated renewal)
- Commercial SSL (Extended validation for enterprise)
- Wildcard certificates (Multiple subdomains)
Implementation:
### Install Certbot for Let's Encrypt
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx
### Generate certificate
sudo certbot --nginx -d your-domain.com
### Automatic renewal
sudo crontab -e
0 12 * * * /usr/bin/certbot renew --quiet
Authentication and Access Control
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Mandatory for admin users, recommended for all users:
- TOTP apps (Google Authenticator, Authy)
- SMS backup (for account recovery)
- Backup codes (printed and secured)
Single Sign-On (SSO) Integration: For enterprise deployments, integrate with your existing identity provider:
- SAML 2.0: Works with Azure AD, Okta, Google Workspace
- OAuth 2.0: Direct integration with cloud providers
- LDAP: Legacy enterprise directory services
Database Security:
### Odoo configuration for database encryption
db_sslmode = require
db_host = your-db-server.com
db_port = 5432
db_user = odoo_secure_user
Network Security
Firewall Configuration:
### Allow only necessary ports
ufw allow ssh
ufw allow 'Nginx Full'
ufw deny 8069 # Block direct Odoo access
ufw enable
VPN Access for Administration: Set up WireGuard or OpenVPN for administrative access:
- Separate admin network segment
- Logged and monitored connections
- Regular access reviews
Odoo Implementation DevOps Best Practices
2025 implementations shine here.
Modern DevOps practices revolutionize Odoo deployment from a manual process into a reliable, automated system.
Docker Containerization
Every production Odoo deployment must use containers because:
Benefits:
- Consistent environments across dev/staging/production
- Easy rollbacks when updates fail
- Simplified backup and disaster recovery
- Scalable infrastructure
Production Docker Setup: Research and testing produced a complete Docker Compose configuration that handles:
- Odoo 18 application container
- PostgreSQL 15 database container
- Nginx reverse proxy with SSL
- Health checks and auto-restart
- Log aggregation
Download the complete Docker configuration:
wget /assets/downloads/odoo-docker-compose.yml
CI/CD Pipeline Implementation
GitLab CI/CD Pipeline (Recommended):
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy
build_image:
stage: build
script:
- docker build -t $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:$CI_COMMIT_SHA .
- docker push $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:$CI_COMMIT_SHA
test_modules:
stage: test
script:
- docker run --rm $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:$CI_COMMIT_SHA odoo --test-enable --stop-after-init
deploy_production:
stage: deploy
script:
- docker-compose up -d
only:
- main
Automated Testing:
- Unit tests for custom modules
- Integration tests for workflows
- Performance tests for database queries
- Security scanning for vulnerabilities
Monitoring and Alerting
Essential Monitoring:
- Application: Response time, error rates, user sessions
- Database: Connection count, query performance, disk usage
- System: CPU, RAM, disk space, network bandwidth
- Business: Failed transactions, data quality issues
Alerting Thresholds:
### Prometheus alerting rules
- alert: OdooHighResponseTime
expr: http_request_duration_seconds{job="odoo"} > 5
for: 2m
- alert: PostgreSQLConnections
expr: postgresql_connections{state="active"} > 150
for: 5m
- alert: DiskSpaceHigh
expr: disk_used_percent > 85
for: 10m
Backup and Disaster Recovery
This protects your business. When everything crashes (hardware failure, ransomware, human error), your backup strategy determines whether you lose a few hours or a few months of work.
Backup Strategy
The 3-2-1 Rule Applied to Odoo:
- 3 copies of your data (production + 2 backups)
- 2 different storage media (local + cloud)
- 1 offsite backup (different geographic location)
What to Backup:
- Database: Daily full backup, hourly incremental
- File Storage: All uploaded documents and attachments
- Configuration: Odoo config files, custom modules
- SSL Certificates: For quick recovery
Automated Backup Script: Download the complete backup script:
wget /assets/downloads/basic_odoo_backup.sh
chmod +x basic_odoo_backup.sh
Key features of the backup script:
- Daily full database backups
- File storage and configuration backup
- Cloud storage sync (AWS S3 compatible)
- Automatic cleanup of old backups
- Email notifications on backup failure
Disaster Recovery Testing
Monthly DR Testing:
- Restore database to staging environment
- Verify all modules load correctly
- Test critical business workflows
- Document recovery time and any issues
Recovery Time Objectives:
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective): 4 hours maximum
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective): 1 hour maximum data loss
System Performance Optimization
We separate the systems that work from the systems that work well here. Performance optimization isn’t about making Odoo faster—it’s about making your business more responsive.
Database Optimization
PostgreSQL Configuration for Odoo:
# /etc/postgresql/15/main/postgresql.conf
max_connections = 200
shared_buffers = 256MB # 25% of 1GB RAM
effective_cache_size = 768MB # 75% of 1GB RAM
work_mem = 4MB
maintenance_work_mem = 256MB
checkpoint_completion_target = 0.9
wal_buffers = 16MB
default_statistics_target = 100
Index Optimization: Monitor slow queries and add indexes strategically:
-- Common Odoo indexes that improve performance
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY idx_account_move_line_date
ON account_move_line (date);
CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY idx_product_template_active
ON product_template (active) WHERE active = true;
Application Server Tuning
Odoo Worker Configuration:
### /etc/odoo.conf
workers = 2 * CPU_cores + 1
max_cron_threads = 2
limit_memory_hard = 2684354560 # 2.5GB
limit_memory_soft = 2147483648 # 2GB
limit_request = 8192
limit_time_cpu = 600
limit_time_real = 1200
Nginx Optimization: Download the complete production-ready Nginx configuration:
wget https://ariashaw.com/assets/downloads/nginx-odoo.conf
Key optimizations include:
- Static file caching (1 month expiry)
- Gzip compression for all text content
- Rate limiting for login attempts
- WebSocket support for longpolling
Getting Started: Your Technical Implementation Plan
Your step-by-step technical implementation plan:
Week 1: Infrastructure Setup
- Provision servers (cloud or on-premise)
- Install base operating system (Ubuntu 22.04 LTS)
- Configure networking and security groups
- Set up monitoring and alerting
Week 2: Odoo Installation
- Install PostgreSQL and configure database
- Install Odoo 18 using our automated script
- Configure Nginx reverse proxy
- Set up SSL certificates
- Implement backup strategy
Week 3: Security Hardening
- Configure 2FA for all users
- Set up VPN access for administrators
- Implement database encryption
- Configure audit logging
- Run security vulnerability scan
Week 4: Testing and Optimization
- Performance testing with expected user load
- Disaster recovery testing
- Security penetration testing
- Documentation of all configurations
Download the complete installation script:
wget /assets/downloads/odoo-install.sh
chmod +x odoo-install.sh
sudo ./odoo-install.sh
Common Technical Pitfalls to Avoid
Before we move to data migration, these technical mistakes sabotage implementations:
- Undersizing PostgreSQL: Allocate more RAM to the database server than the application server
- Ignoring backup testing: Backups that won’t restore serve no purpose
- Skipping staging environment: Validate in staging before production
- Poor monitoring setup: You can’t fix what you can’t see
- Inadequate security review: Integrate security from the start rather than bolting it on later
In the next phase, we’ll tackle data migration and system integration—the technical challenges that make or break most implementations. With your technical foundation established, you’re ahead of 80% of Odoo implementations.
Phase 3: Data Migration & System Integration
You’re facing what implementation teams consider the “make or break” phase.
Implementation case studies show that planned Odoo implementations crash here—not because of bad technology, but because teams underestimated the complexity of moving live business data from one system to another while keeping operations running.
Case studies document scenarios where data migration appears to complete, but post-go-live analysis exposes critical issues: 40% of historical sales data missing, incorrect inventory counts, and corrupted customer contact information.
These situations result in weeks of business disruption and tens of thousands in recovery costs, highlighting that “migration complete” and “migration correct” are different things.
If you’re dealing with substantial business data—customer records, financial history, inventory levels, or complex integrations—this phase will determine whether your Odoo implementation becomes a success story or a cautionary tale.
This phase proves critical because unlike other phases where you can iterate and improve, data migration demands a one-shot operation.
Get it wrong, and you’re trapped with corrupted data or facing the expensive prospect of starting over.
Get it right, and you’ve built the foundation for everything else to work seamlessly.
How to Migrate Data to Odoo: Planning Your Strategy
Data migration analysis collapses when teams treat it like a technical task rather than a business process. It’s not about moving files from Point A to Point B—it’s about preserving the business intelligence embedded in your current systems while adapting it to Odoo’s way of organizing information.
Understanding What You’re Migrating
Before touching a single record, you must map what data you have and what it means to your business operations.
Four Types of Business Data:
- Master Data: Your core business entities (customers, products, vendors, employees)
- Transactional Data: Your business activity history (orders, invoices, payments)
- Reference Data: Your business rules and configurations (accounts, taxes, workflows)
- Historical Data: Your business intelligence (metrics, trends, analytics)
Critical Assessment Questions:
- How clean is your current data and when was it last audited?
- How much historical data is required vs needed?
- Which systems feed data into your current setup and how will migration affect them?
- What’s your acceptable downtime window for business operations?
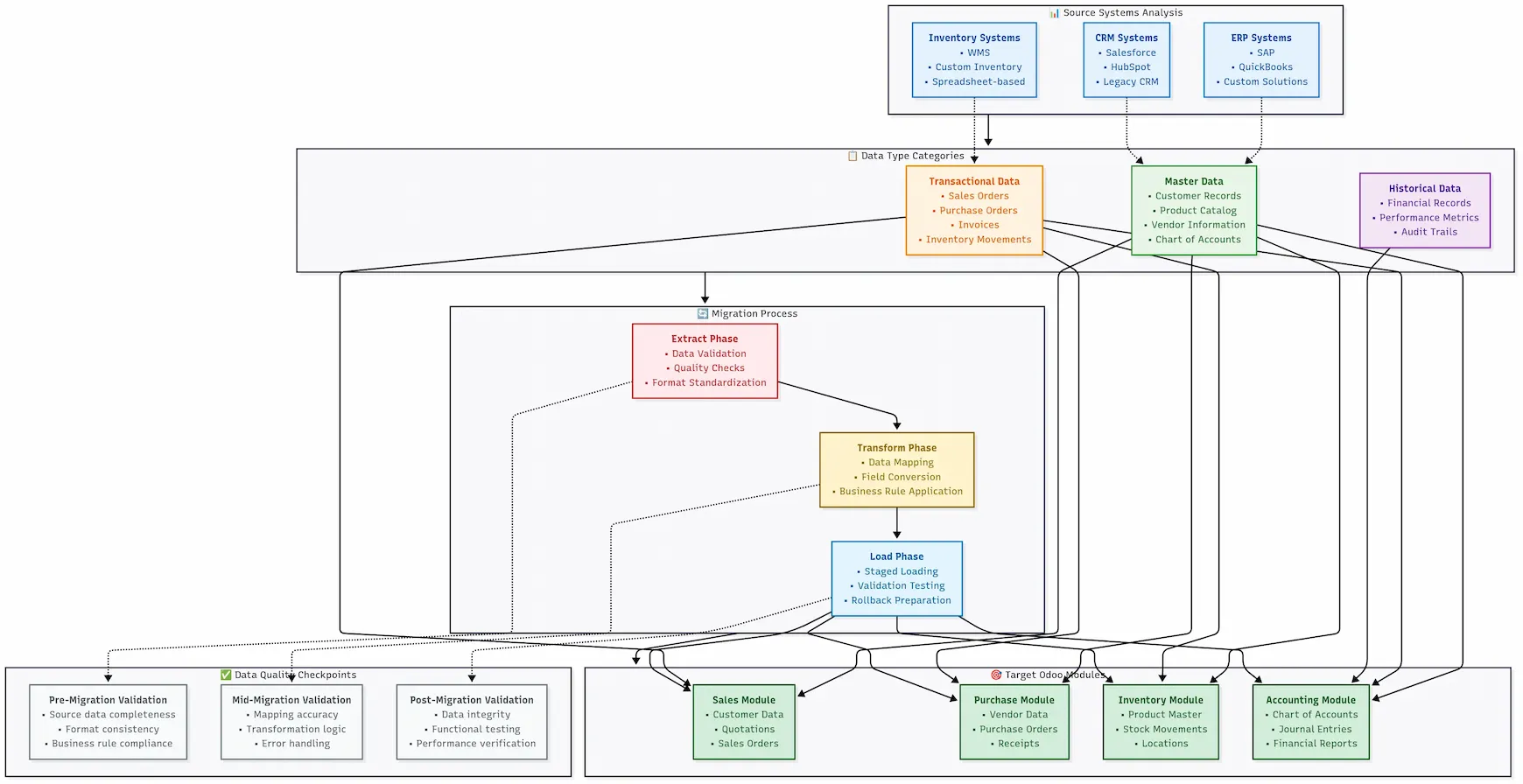 Comprehensive data migration strategy showing how different data types flow from legacy systems into Odoo modules
Comprehensive data migration strategy showing how different data types flow from legacy systems into Odoo modules
Data Migration Risk Assessment
Use our assessment tools to detect migration pitfalls before they become expensive problems:
🔍 Migration Risk Assessor - Analyze database size, module complexity, and PostgreSQL version compatibility
High-Risk Scenarios:
- Databases larger than 100GB with complex relationships
- Legacy systems with custom field structures requiring translation
- Real-time integration requirements during migration windows
- Multi-currency or multi-company configurations with interdependencies
Medium-Risk Scenarios:
- Standard business data with minor customizations
- Historical data spanning 3-5 years requiring archival decisions
- Basic third-party integrations with API dependencies
Low-Risk Scenarios:
- Clean, well-structured data under 10GB
- Recent data (under 2 years) with standard formats
- Minimal customizations using standard Odoo functionality
Odoo Data Migration from Excel CSV and QuickBooks Guide
Phase 3A: Comprehensive Database Migration
For complete database migration with zero-downtime strategies, deploy our methodology:
🎯 Complete Migration Procedures: Our dedicated Odoo Database Migration Guide provides the complete 13-step process, including pre-migration assessment, staging validation, production execution, and post-migration verification—all tested across 300+ successful migrations.
Migration Overview:
- Risk Assessment & Planning (Steps 1-3): Compatibility verification and data cleanup
- Backup Strategy (Steps 4-6): Database, filestore, and configuration backup
- Target Server Optimization (Steps 7-9): Hardware sizing and PostgreSQL tuning
- Zero-Downtime Execution (Steps 10-13): Staging validation and production migration
Key Migration Tools Available:
- 📊 Environment Compatibility Checker - Verify system requirements
- 🧹 Data Cleanup Toolkit - Fix data integrity issues
- 💾 Complete Backup System - Enterprise-grade backup with verification
Phase 3B: CSV/Excel Data Import Best Practices
For importing business data from spreadsheets and legacy systems:
Data Preparation Strategy:
- Clean and standardize data formats (phone numbers, emails, currencies)
- Map fields to Odoo’s data structure requirements
- Test with small batches before full import
- Validate results with SQL queries and spot checks
Common Import Challenges:
- Duplicate records violating unique constraints
- Missing references causing foreign key errors
- Format mismatches between source and target systems
- Large datasets overwhelming server resources
Professional Import Tools:
- 🔍 Data Cleanup Toolkit - Automated data cleaning and validation
- 🌐 API Diagnostics Tool - Basic API connectivity and SSL validation
Phase 3C: Legacy System Integration Strategy
For complex migrations from older ERP systems:
Advanced Migration Approach:
- Multi-table relationship mapping with referential integrity preservation
- Custom field translation between different system architectures
- Incremental migration with rollback capabilities
- Automated testing and verification at each stage
Professional Migration Tools:
- 🚀 Production Migration Executor - Zero-downtime migration with automatic rollback
- 🏗️ Staging Environment Validator - Seven-layer validation before production
- ⚡ Performance Validation Suite - 24-hour performance monitoring
Third-Party Integrations
Modern businesses demand integration with payment processors, shipping providers, accounting systems, and specialized business tools. Odoo 18’s enhanced API capabilities provide integration approaches:
Integration Complexity Assessment
Real-time Sync Required: Payment gateways, inventory systems, CRM platforms Batch Processing Acceptable: Accounting systems, reporting tools, backup services One-way Data Flow: Analytics platforms, business intelligence tools Bi-directional Complex: E-commerce platforms, multi-location inventory systems
Modern Integration Methods (2025)
Odoo 18 supports four primary integration approaches:
- REST API - Standard web-friendly interface for most integrations
- XML-RPC - Direct function access for legacy system compatibility
- Queued Middleware - Asynchronous, scalable data exchange for high-volume operations
- Webhook Integration - Real-time event-driven updates for immediate synchronization
Common Integration Challenges
Authentication Management: OAuth and token-based systems requiring renewal Data Format Mismatches: Different naming conventions and validation rules Performance Optimization: Managing high-volume data exchange efficiently Error Handling: Graceful degradation when external systems are unavailable
Integration Testing Tools:
- 🌐 API Diagnostics Tool - Basic connectivity testing for external APIs
- 📧 SMTP Configuration Tester - Email system validation and delivery verification
Troubleshooting Migration Issues
Despite planning, migration issues can erupt. Your approach to rapid problem resolution:
5-Step Migration Troubleshooting Process
Step 1: Immediate Health Assessment Database queries to verify record counts and identify corruption
Step 2: Data Integrity Validation Check for broken relationships and orphaned records using referential integrity queries
Step 3: Performance Impact Assessment Monitor database performance metrics to ensure operation
Step 4: Integration Functionality Testing Verify external integrations are working with live data
Step 5: User Acceptance Validation Confirm key users can complete critical business workflows
Emergency Recovery Procedures
When migration crashes, recovery is essential:
Emergency Recovery Tools:
- 🔄 Intelligent Rollback System - Basic rollback with optional data preservation
- 🚨 Emergency Recovery System - Complete disaster recovery toolkit
Data Validation and Quality Assurance
Quality Gates for Migration Success:
- Data Completeness: 100% of critical records migrated
- Data Accuracy: <0.1% error rate in spot-check validation procedures
- Performance Baseline: Response times within 10% of pre-migration metrics
- Integration Functionality: All critical integrations operating correctly
- User Acceptance: Key users completing core workflows without issues
Professional Validation Tools:
- 🔍 Backup Validation Tool - Complete backup integrity verification
- 📊 Backup Quality Calculator - 120-point assessment system
📊 Need comprehensive backup strategies? For production environments, implement enterprise-grade backup procedures detailed in our Odoo Database Backup & Restore Guide, including automated verification, cloud sync, and emergency recovery protocols.
Migration Success Metrics to Track:
Monitor these key indicators throughout your migration:
- Technical Metrics: Data completeness >99%, accuracy >99.9%, performance degradation <10%
- Business Metrics: User adoption >90% within 30 days, process efficiency gain >15%
- Project Metrics: Timeline variance <20%, budget variance <15%, stakeholder satisfaction >8/10
Remember: successful data migration isn’t just about moving data—it’s about transforming how your business operates while maintaining complete operational continuity. The investment in proper migration methodology pays dividends through reduced risk, faster implementation, and higher user adoption rates.
Phase 4: Module Configuration & Business Process Implementation
Most Odoo implementations either soar or explode here.
You’ve migrated your data, but now comes the real challenge: configuring Odoo to match how your business operates, not how the software thinks you should operate.
Implementation failures show that executed technical migrations collapse because teams rushed through this phase, thinking configuration was just “filling out some forms.”
Six months later, users are working around the system instead of with it, productivity has plummeted 30%, and management is questioning the entire investment.
Odoo’s flexibility is both its greatest strength and biggest trap.
With 30,000+ settings across dozens of modules, there are millions of ways to configure your system—and only a few hundred that will work for your business.
This phase is where you translate your business requirements into a working Odoo system that your team will use and love.
Business Process Analysis and Mapping
Before touching a single configuration setting, you need to understand exactly how work flows through your organization—not how you think it flows, but how it flows.
The Reality Check: Documented vs. Actual Processes
Most businesses discover an uncomfortable truth during this phase: their documented processes bear little resemblance to how work gets done. That procedure manual gathering dust? Your team stopped following it two years ago when they found a better way.
Three-Layer Process Discovery Method:
- Official Process Documentation - What management thinks happens
- Actual User Workflows - What happens day-to-day
- Exception Handling - What happens when things go wrong
Critical Questions for Each Business Area:
Sales Process:
- How do leads enter your system and get qualified?
- What approvals are required for quotes, and who provides them?
- How do you handle pricing exceptions and custom discounts?
- What happens when a customer wants to modify an existing order?
Purchasing Process:
- Who can create purchase orders and what are the approval limits?
- How do you handle partial deliveries and back-ordered items?
- What’s your process for handling vendor pricing changes?
- How do you track and approve vendor invoices?
Inventory Management:
- How often do you count inventory and how do you handle discrepancies?
- What’s your process for handling damaged or obsolete stock?
- How do you track serial numbers and lot numbers?
- What approvals are needed for inventory adjustments?
Financial Operations:
- What’s your month-end closing process and timeline?
- How do you handle multi-currency transactions?
- What reports does management need and how frequently?
- How do you track and allocate costs across departments?
Workflow Configuration Strategies
The key to successful Odoo configuration is starting simple and adding complexity gradually. Teams attempting to replicate every nuance of their current process immediately create confusion and failure patterns.
Progressive Configuration Approach:
Phase 1: Core Workflows (Week 1-2) Configure the 20% of functionality that handles 80% of your daily operations:
- Basic customer and product setup
- Standard sales order to invoice workflow
- Simple purchase order to receipt process
- Basic inventory movements
Phase 2: Business Rules (Week 3-4) Add the business logic that makes your processes unique:
- Approval workflows and limits
- Automated actions and notifications
- Custom pricing rules
- Tax configurations and compliance settings
Phase 3: Advanced Features (Week 5-6) Implement the sophisticated features that provide competitive advantage:
- Advanced reporting and dashboards
- Multi-company configurations
- Complex manufacturing workflows
- Integration with external systems
Professional Process Mapping Tools:
- 🧩 Module Compatibility Scanner - Analyze which modules work together
- 🔗 Dependency Analyzer - Resolve module dependency conflicts
- ⚙️ Dependency Resolution Engine - Intelligent module installation order
Core Module Implementation
Chart of Accounts Setup Implementation
Your chart of accounts forms the foundation of your financial system—get this wrong, and you’ll spend years fixing problems.
Critical Success Factors:
Industry-Specific Account Structure: Different industries demand different approaches to account organization. Manufacturing companies need detailed cost accounting, while service businesses focus on project profitability.
Multi-Location Considerations: If you operate in multiple locations, decide early whether you need separate legal entities or can use Odoo’s multi-company features within a single entity.
Tax Configuration Strategy: Tax setup stumbles many implementations. Consider:
- Sales tax vs. VAT requirements
- Multi-jurisdictional tax obligations
- Automated tax calculation vs. manual override needs
- Integration with tax preparation software
Professional Configuration Tools:
- 📊 Server Specifications Calculator - Ensure adequate resources for your module load
- 🔧 Final Verification Checklist - Validate complete configuration
CRM Implementation Strategy
Modern CRM extends beyond storing contact information—it creates a predictable revenue machine.
Lead Management Configuration:
- Define lead sources and tracking methods
- Set up lead scoring and qualification criteria
- Configure automated lead assignment rules
- Establish lead nurturing workflows
Opportunity Pipeline Design:
- Map your sales stages to Odoo’s opportunity workflow
- Define probability percentages for each stage
- Set up automated reminders and escalations
- Configure revenue forecasting and reporting
Customer Communication Management:
- Set up email templates for common communications
- Configure automated follow-up sequences
- Establish customer portal access and permissions
- Design customer satisfaction tracking
Sales Module Implementation
Your sales module configuration directly impacts revenue generation—every inefficiency here costs money.
Quote-to-Cash Optimization:
- Streamline quote creation with product catalogs and pricing rules
- Configure approval workflows for discount exceptions
- Set up automated order confirmation and fulfillment
- Establish invoice generation and payment tracking
Sales Team Management:
- Define sales territories and assignment rules
- Set up commission tracking and calculation
- Configure sales reporting and dashboards
- Establish performance metrics and KPIs
Accounting Module Implementation
Financial reporting anchors business decision-making.
Financial Workflow Configuration:
- Set up automated invoice posting and reconciliation
- Configure multi-currency handling and revaluation
- Establish bank reconciliation procedures
- Design month-end closing workflows
Compliance and Reporting:
- Configure statutory reporting requirements
- Set up audit trails and approval workflows
- Establish financial controls and segregation of duties
- Design management reporting dashboards
Advanced Module Configuration
Inventory Management Implementation
Modern inventory management transcends tracking quantities—it’s about optimizing cash flow and service levels.
Warehouse Operations:
- Configure picking strategies and routing
- Set up cycle counting and inventory adjustments
- Establish reorder points and procurement rules
- Design inventory valuation methods
Quality Control Integration:
- Set up incoming inspection procedures
- Configure quality control checkpoints
- Establish non-conformance handling
- Design quality reporting and metrics
Manufacturing Module Implementation
Manufacturing in Odoo demands balance between flexibility and control.
Production Planning:
- Configure master production schedule
- Set up capacity planning and resource allocation
- Establish bill of materials and routing management
- Design work order tracking and reporting
Shop Floor Integration:
- Set up barcode scanning and mobile access
- Configure time and attendance tracking
- Establish quality control checkpoints
- Design production reporting dashboards
Project Management Implementation
Project-based businesses need different configuration approaches than product-based companies.
Project Lifecycle Management:
- Configure project templates and phases
- Set up resource allocation and scheduling
- Establish timesheet tracking and approval
- Design project profitability analysis
Client Collaboration:
- Set up customer portal access
- Configure project communication workflows
- Establish milestone tracking and billing
- Design client reporting and dashboards
HR Module Configuration
HR configuration affects every employee—get it right and boost productivity, get it wrong and create frustrations.
Employee Lifecycle Management:
- Configure recruitment and onboarding workflows
- Set up performance review processes
- Establish time-off approval procedures
- Design employee self-service capabilities
Payroll Integration:
- Configure pay structure and benefits
- Set up automated payroll processing
- Establish compliance reporting
- Design HR analytics and reporting
Customization and Development
When to Customize vs. Configure
This question determines whether your Odoo implementation becomes a strategic asset or expensive liability.
Configure First, Customize Last: Odoo’s functionality handles 90% of business requirements. The temptation to customize is strong, but resist it. Why:
- Features Get Updates: Odoo releases enhance functionality—customizations don’t
- Maintenance Complexity: Each customization demands maintenance and testing
- User Training: Odoo documents and supports workflows—custom ones receive no support
- Integration Challenges: Third-party integrations mesh with Odoo, not your customizations
Customization Makes Sense When:
- Competitive Advantage: The feature delivers competitive differentiation
- Regulatory Compliance: Legal requirements that Odoo can’t satisfy
- Critical Workflow: Core business process that can’t adapt to Odoo’s approach
- ROI Justification: Financial benefit that outweighs customization and maintenance costs
Development Best Practices
If you customize, execute it right:
Modular Development Approach:
- Create separate modules for each customization
- Follow Odoo’s coding standards and conventions
- Document all customizations
- Plan for Odoo version upgrades
Testing and Quality Assurance:
- Set up automated testing for customizations
- Test customizations with data and workflows
- Verify compatibility with other modules
- Plan rollback procedures for failed customizations
Professional Development Tools:
- 🧩 Module Compatibility Scanner - Test custom module compatibility
- 🔍 Safe OpenUpgrade Wrapper - Upgrade safely with customizations
- 🔗 Dependency Analyzer - Resolve complex module dependencies
Solving Common Customization Problems
Problem: Custom Module Conflicts Multiple custom modules interfering with each other demand systematic conflict resolution:
- Pinpoint conflicting functionalities using dependency analysis
- Prioritize modules by business impact
- Redesign conflicting modules to coexist
- Validate in staging environment
Problem: Upgrade Compatibility Custom modules shatter during Odoo version upgrades:
- Maintain detailed customization documentation
- Test upgrades in isolated environments
- Plan customization updates alongside Odoo upgrades
- Consider migrating to functionality when possible
Professional Problem-Solving Tools:
- ⚙️ Dependency Resolution Engine - Intelligent conflict resolution
- 🛡️ Database Corruption Detector - Detect issues before they spread
- 🔄 Intelligent Rollback System - Basic rollback for failed customizations
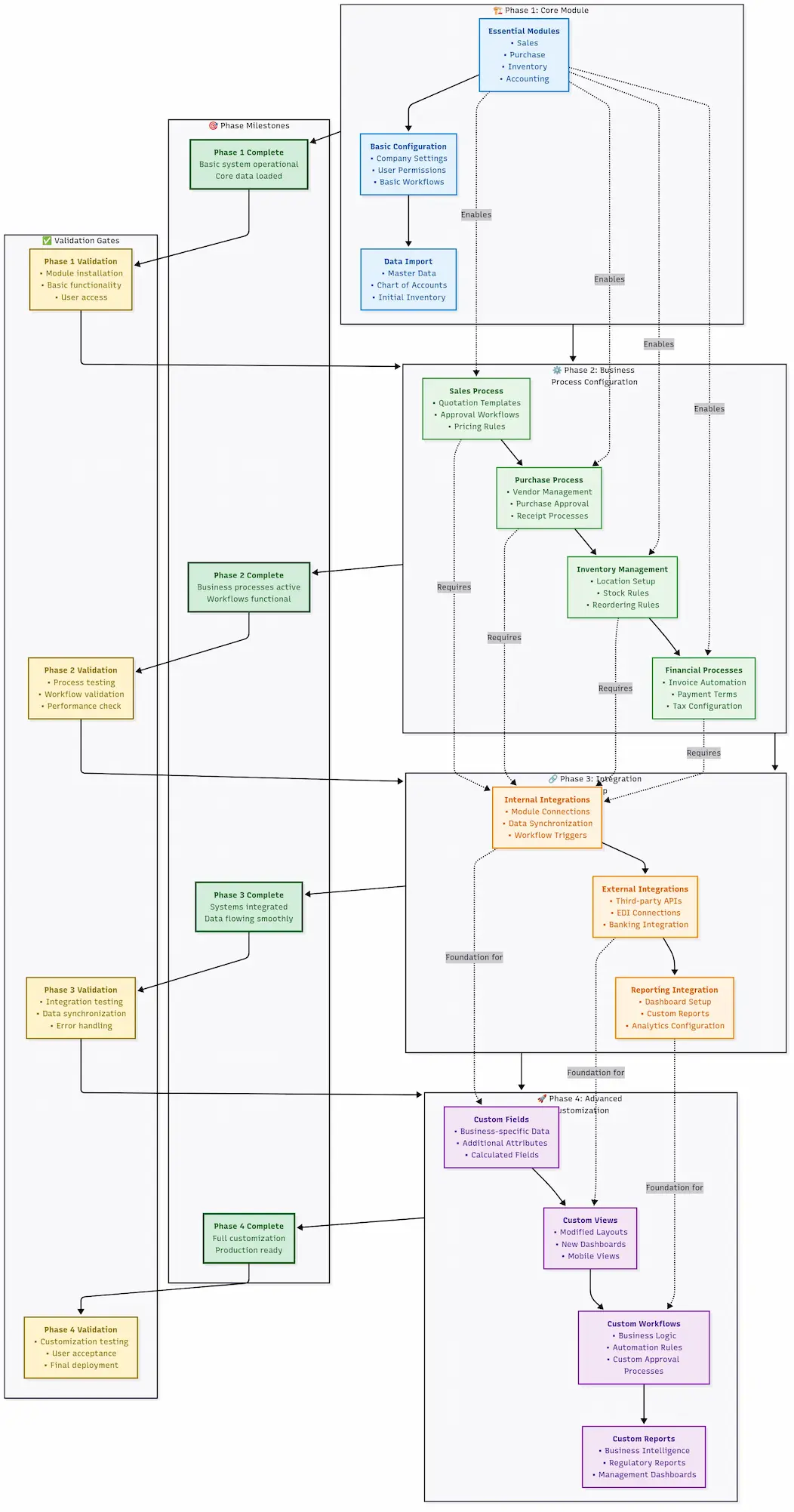 Progressive module configuration workflow from basic setup through advanced customization and quality assurance
Progressive module configuration workflow from basic setup through advanced customization and quality assurance
Configuration Success Metrics:
Track indicators to ensure your configuration works:
- User Adoption Rate: >90% of users actively using configured features
- Process Efficiency: 20-30% reduction in task completion time
- Data Quality: <2% error rate in configured workflows
- System Performance: Response times under 3 seconds for configured processes
- Training Requirements: <4 hours training needed for new user productivity
Phase 4 Completion Checklist:
Before moving to user training, ensure core business processes are configured and tested, user permissions are set, essential reports are created, and integration points are functional.
Remember: perfect configuration is the enemy of good configuration. Start with 80% of your requirements working smoothly, then iterate and improve based on real user feedback. A system that works well for most processes beats a configured system that never gets deployed.
Phase 5: User Training & Change Management
The brutal truth about Odoo implementations: you can have the most configured system in the world, but if your users don’t adopt it, you’ve built an expensive monument to failure.
Implementation failures show that flawless systems die slow deaths because teams dismiss user training as an afterthought—a quick session the week before go-live where someone clicks through screens while confused employees scribble notes.
Six months later, users maintain shadow spreadsheets “just in case,” productivity is down 40%, and management is questioning the investment.
Successful Odoo implementation isn’t about the technology—it’s about changing how people work.
Changing how people work is one of the hardest challenges in business.
Research reveals from implementations: when you approach training and change management systematically, user adoption rates exceed 95%, productivity increases within 30 days, and employees become advocates instead of resistors.
This phase transforms your technical Odoo implementation into a business transformation that delivers real results.
How to Train Users on Odoo Implementation
Most training programs fail because people who understand the system design them for people who’ve never seen it.
Like having a Formula 1 driver teach a teenager how to parallel park—the expert has forgotten what confusion feels like.
Understanding Who Needs What Training
Not everyone needs to know everything about Odoo.
A warehouse worker doesn’t need to understand financial reporting, and your CFO doesn’t need to know how to pick inventory.
Role-based training is more effective and less overwhelming.
The Four Training Personas:
Power Users (5-10% of users):
- Department managers and system administrators
- Need deep understanding of their modules
- Training focus: Advanced features, customization, troubleshooting
- Training time: 2-3 days intensive + ongoing support
Daily Users (60-70% of users):
- Staff who use Odoo for core daily tasks
- Need solid understanding of their specific workflows
- Training focus: Essential features, common tasks, basic troubleshooting
- Training time: 1 day intensive + follow-up sessions
Occasional Users (20-30% of users):
- Users who access Odoo weekly or monthly
- Need basic navigation and specific task completion
- Training focus: Simple workflows, finding information, getting help
- Training time: 4-6 hours across multiple sessions
Read-Only Users (5-10% of users):
- Executives and external stakeholders
- Need access to reports and dashboards
- Training focus: Interpretation of data, basic navigation
- Training time: 1-2 hours demonstration
Role-Based Training Approaches
Training Delivery Methods:
Hands-On Workshops (Most Effective):
- Small groups (6-8 people maximum)
- Real scenarios using actual company data
- Immediate feedback and problem-solving
- Practice time with trainer support
Just-in-Time Training:
- Brief focused sessions right before process changes
- Quick reference guides and video tutorials
- Peer mentoring and buddy systems
- Progressive skill building over time
Self-Paced Learning:
- Online modules and documentation
- Video libraries for common tasks
- Interactive tutorials and simulations
- Flexible scheduling for different roles
Department-Specific Training
Sales Team Implementation Impact
Sales teams resist new systems because they see them as obstacles to closing deals. Your approach must demonstrate immediate value, not just long-term benefits.
Sales Training Focus Areas:
Lead Management Efficiency:
- Show how Odoo captures leads (versus manual entry)
- Demonstrate lead scoring and qualification workflows
- Practice converting leads to opportunities in under 60 seconds
- Train on automated follow-up and nurturing sequences
Quote Creation Speed:
- Master product catalog navigation and search
- Practice quote generation with pricing rules and discounts
- Learn approval workflows for exceptional pricing
- Train on quote tracking and follow-up automation
Pipeline Management:
- Understanding opportunity stages and probability
- Forecasting and reporting for accurate predictions
- Activity scheduling and reminder management
- Performance tracking and goal monitoring
Sales Training Success Metrics:
- Quote generation time reduced by 50%
- Lead response time under 2 hours
- Pipeline accuracy improved to 85%+
- User adoption rate exceeding 90% within 30 days
Manufacturing Operations Training
Manufacturing teams require training that connects shop floor reality with system requirements. They think in terms of physical processes, not database records.
Manufacturing Training Focus:
Work Order Management:
- Connecting production schedules to actual manufacturing
- Recording time, materials, and quality data
- Understanding how shop floor data affects planning
- Troubleshooting common data entry problems
Inventory Integration:
- Real-time inventory updates from production
- Quality control checkpoints and non-conformance handling
- Traceability and lot tracking requirements
- Managing work-in-process and finished goods
Reporting and Analytics:
- Production efficiency metrics and trending
- Cost tracking and variance analysis
- Quality metrics and improvement tracking
- Capacity planning and resource optimization
Financial Reporting Training
Finance teams are the most demanding users—they need accuracy, compliance, and detailed reporting capabilities.
Finance Training Focus:
Daily Operations:
- Invoice processing and approval workflows
- Bank reconciliation procedures and automation
- Journal entry creation and corrections
- Multi-currency transactions and revaluation
Period Closing:
- Month-end closing procedures and checklists
- Automated accruals and deferrals
- Financial statement generation and review
- Audit trail documentation and compliance
Management Reporting:
- Dashboard creation and customization
- KPI tracking and variance analysis
- Budget vs. actual reporting
- Cash flow forecasting and analysis
HR Processes Training
HR implementations affect every employee, so training must be broad but not overwhelming.
HR Training Focus:
Employee Self-Service:
- Time-off requests and approval workflows
- Timesheet submission and project tracking
- Personal information updates and maintenance
- Performance review participation and documentation
HR Administration:
- Employee onboarding and offboarding processes
- Benefits administration and tracking
- Performance review scheduling and management
- Compliance reporting and documentation
Odoo Implementation Change Management and User Adoption
Improving User Adoption Rates
High adoption rates don’t happen by accident.
They’re the result of change management that tackles rational and emotional barriers to change.
Psychology of System Adoption:
Rational Barriers:
- “I don’t know how to use this system”
- “This seems more complicated than our old way”
- “I can’t find what I need”
Emotional Barriers:
- “I was good at the old system, now I feel stupid”
- “Nobody asked me what I thought about this change”
- “I’m worried I’ll make mistakes and get in trouble”
Addressing Rational Barriers:
Competency Building:
- Progressive skill development from basic to advanced
- Just-in-time training when users need specific capabilities
- Quick reference guides and cheat sheets
- Peer mentoring and support networks
Efficiency Demonstration:
- Side-by-side comparisons of old vs. new processes
- Timing exercises demonstrating speed improvements
- Examples of eliminated duplicate work
- Quantified productivity gains
Addressing Emotional Barriers:
Involvement and Ownership:
- Include users in configuration decisions
- Recognize early adopters and champions
- Celebrate small wins and improvements
- Provide safe spaces to ask questions and make mistakes
Support and Safety:
- Extended support during transition period
- Clear escalation paths for problems
- Regular check-ins and feedback sessions
- Patience with learning curves and mistakes
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Every implementation faces resistance.
The key is identifying it and crushing it rather than hoping it goes away.
Resistance Types:
Active Resistance:
- Vocal complaints about the new system
- Requests to delay or cancel implementation
- Comparisons to “better” alternatives
- Attempts to maintain old processes alongside new ones
Passive Resistance:
- Slow adoption of new processes
- Minimal effort in training sessions
- Continued use of workarounds
- “Malicious compliance” with new procedures
Resistance Management Strategies:
Early Engagement:
- Include potential resistors in planning processes
- Attack concerns before they become entrenched
- Provide support and training
- Transform them into allies and champions
Clear Communication:
- Explain the why behind changes, not just the what
- Share success stories from similar organizations
- Be honest about challenges and timeline
- Deliver updates on progress and benefits
Incentive Alignment:
- Link performance metrics to system adoption
- Recognize and reward early adopters
- Make old processes unavailable or inconvenient
- Provide career development opportunities for system expertise
User Acceptance Testing for Implementation
User acceptance testing transcends finding bugs.
It’s about building confidence and ownership in the system.
UAT Strategy:
Real-World Scenarios:
- Use company data and situations
- Test workflows from start to finish
- Include exception handling and error scenarios
- Verify integration points with other systems
User-Driven Testing:
- Empower users to design their own test scenarios
- Champion exploration and experimentation
- Capture feedback and improvement suggestions
- Refine based on user input before go-live
Professional Testing Tools:
- ⚡ Performance Validation Suite - Monitor system performance during UAT
- 🔧 Final Verification Checklist - Comprehensive pre-go-live validation
Mobile and Remote Access Setup
Modern workforces are mobile and distributed.
Your Odoo implementation must support users wherever they work.
Odoo Mobile App Implementation Setup
The Odoo mobile app transcends a mobile-friendly website.
It’s a purpose-built tool for mobile workflows.
Mobile-First Use Cases:
Field Sales:
- Customer visit planning and routing
- On-site quote generation and approval
- Order entry with real-time inventory checking
- Photo documentation and note-taking
Warehouse Operations:
- Inventory counting and adjustments
- Pick list management and barcode scanning
- Receiving and put-away operations
- Quality control checkpoints
Service Management:
- Work order access and updates
- Time tracking and expense reporting
- Customer signature capture
- Photo documentation of completed work
Mobile Configuration Best Practices:
- Workflows optimized for small screens
- Offline capability for areas with connectivity issues
- Barcode scanning integration for data entry
- Push notifications for tasks and approvals
Remote User Training Considerations
Remote training demands different approaches and tools than in-person sessions.
Remote Training Strategies:
Virtual Hands-On Sessions:
- Screen sharing with hands-on practice
- Breakout rooms for small group work
- Recording sessions for later review
- Interactive polls and Q&A sessions
Self-Paced Digital Learning:
- Video tutorials for common tasks
- Interactive simulations and practice environments
- Progress tracking and competency verification
- Just-in-time support resources
Ongoing Support Systems:
- Virtual office hours for questions
- Peer support forums and communities
- Regular check-in calls and feedback sessions
- Remote screen sharing for troubleshooting
Remote Training Success Tools:
- 💗 Advanced Odoo Health Monitor - Monitor system performance for remote users
- 📈 Monthly Health Check - Regular system review with remote access validation
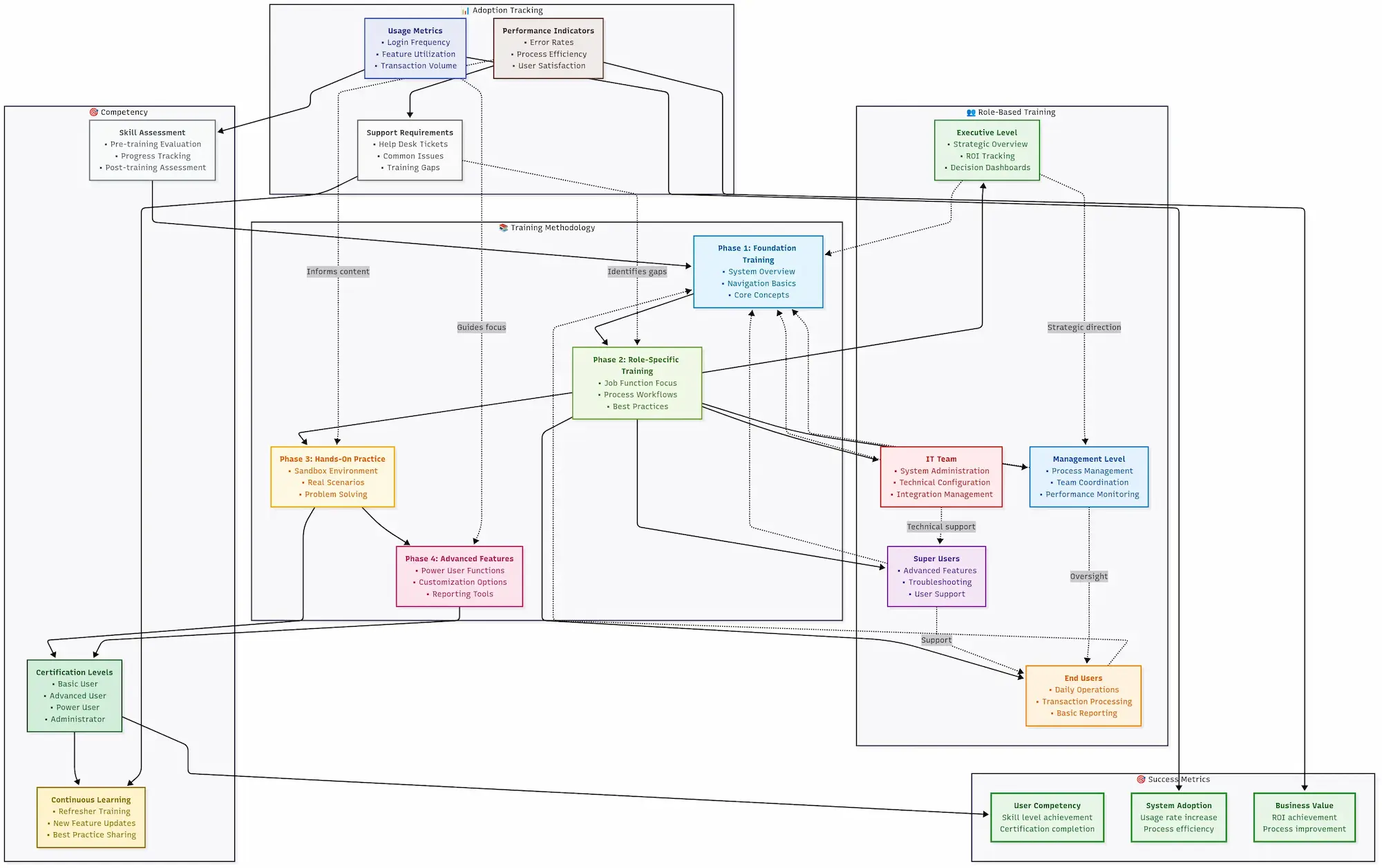 Comprehensive training framework showing role-specific learning paths and adoption tracking methodologies
Comprehensive training framework showing role-specific learning paths and adoption tracking methodologies
Training Success Metrics:
Track these indicators to ensure your training is effective:
- Adoption Rate: >95% of users completing core tasks within 30 days
- Competency Level: Users completing standard tasks without assistance
- Error Reduction: <5% error rate in system transactions
- User Satisfaction: >8/10 rating for system usability and training quality
- Productivity Metrics: Return to baseline productivity within 2-4 weeks
Phase 5 Completion Checklist:
Before go-live, verify that all user groups completed appropriate training, power users are competent, teams establish support procedures, and user acceptance testing is complete with stakeholder sign-off.
Remember: training isn’t a one-time event—it’s an ongoing process. Plan for refresher training, new user onboarding, and continuous skill development. The most successful implementations treat training as an investment in long-term adoption and productivity, not a checkbox to complete before go-live.
Phase 6: Go-Live, Support & Continuous Optimization
This is it—the moment your team has been working toward.
What distinguishes implementations from expensive disasters: understanding that go-live isn’t the finish line, it’s the starting gun.
Analysis of implementation outcomes reveals that prepared implementations can collapse on go-live day when teams treat it as a celebration instead of the beginning of the critical phase.
Conversely, implementations with minor technical issues flourish when they have robust support structures and optimization processes in place.
The brutal reality: the first 90 days after go-live determine whether your Odoo implementation becomes a strategic advantage or an expensive lesson.
During this period, you’ll uncover issues no testing could have predicted, users will push the system in ways you never imagined, and business demands will evolve faster than your configuration.
When you approach go-live with the right validation, support, and optimization strategies, magic happens: your system doesn’t just work—it evolves every day.
Odoo Implementation Validation Testing
Hours before go-live, adrenaline peaks and common sense disappears. Teams rush to make “one last change” or skip validation steps because they’re behind schedule. Disciplined validation processes save implementations.
Implementation Validation Testing
Your validation extends beyond checking if features work—it’s verifying that your business can operate through Odoo under real-world conditions.
72-Hour Pre-Go-Live Protocol:
72 Hours Before: Systems Check
- Run complete backup and verify restoration procedures
- Execute full system performance validation under simulated load
- Verify all integrations are functional and responsive
- Confirm all user accounts and permissions are configured
- Test disaster recovery procedures and rollback plans
48 Hours Before: Process Validation
- Execute end-to-end business workflows with real data
- Validate reporting accuracy against known historical data
- Test exception handling for unusual but realistic scenarios
- Confirm mobile access and remote connectivity
- Verify backup systems and monitoring alerts are active
24 Hours Before: Readiness Review
- Conduct go/no-go decision meeting with all stakeholders
- Review support staffing and escalation procedures
- Confirm communication plans for users and customers
- Validate rollback procedures and decision criteria
- Execute final data synchronization and cutover preparation
Professional Validation Tools:
- 🔧 Final Verification Checklist - Comprehensive pre-go-live system validation
- ⚡ Performance Validation Suite - 24-hour performance monitoring
- 🏗️ Staging Environment Validator - Complete staging environment verification
User Acceptance Testing Procedures
User acceptance testing at this stage extends beyond finding bugs—it’s about building confidence and identifying training needs.
UAT Focus Areas:
Business-Critical Workflows:
- Order-to-cash process with actual customer data
- Purchase-to-pay cycle with real vendor information
- Month-end closing procedures with current period data
- Inventory management with live stock levels
Exception Scenarios:
- System behavior during peak usage periods
- Error handling when external integrations fail
- Data recovery procedures after user errors
- Performance under realistic concurrent user loads
User Confidence Building:
- Empower power users to demonstrate system mastery
- Resolve user concerns or questions
- Validate that job aids and quick reference materials are accessible
- Ensure escalation paths for post-go-live support are clear
Performance Testing and Optimization
Your system might work with 5 test users, but what happens when 50 users start working during month-end closing?
Production Load Testing:
Concurrent User Simulation: Test with 150% of expected concurrent users to ensure performance headroom. Modern businesses have usage spikes during critical periods that exceed planning assumptions.
Database Performance Under Load:
- Query execution times under data volumes
- Response times for reports with datasets
- Performance of batch processes during business hours
- Impact of backup operations on user experience
Integration Performance:
- Third-party API response times under load
- Network latency impact on remote users
- Mobile app performance with poor connectivity
- Synchronization delays between integrated systems
Professional Performance Tools:
- 💗 Advanced Odoo Health Monitor - Real-time performance monitoring
- 📈 Monthly Health Check - Comprehensive system health assessment
- 🔧 PostgreSQL Production Tuning - Database optimization for production loads
Odoo Implementation Support and Maintenance
The quality of your post-go-live support determines whether users become advocates or saboteurs of your system.
Setting Up Internal Support Structures
Three-Tier Support Model:
Tier 1: Immediate User Support (Response: <2 hours)
- Power users from each department
- Handle basic questions and common issues
- Escalate complex problems to Tier 2
- Sustain user confidence and momentum
Tier 2: Technical Configuration Support (Response: <4 hours)
- IT team members with deep Odoo knowledge
- Crush configuration issues and minor customizations
- Coordinate with external partners when needed
- Manage system performance and optimization
Tier 3: Strategic Development Support (Response: <24 hours)
- External consultants or internal developers
- Master complex customizations and integrations
- Plan future enhancements and system evolution
- Deliver expert guidance on business process optimization
Support Communication Framework:
Daily Stand-ups (First 30 Days):
- Analyze previous day’s issues and resolutions
- Discover emerging patterns or systemic problems
- Prioritize support activities for maximum impact
- Communicate status to stakeholders and users
Weekly Optimization Reviews (First 90 Days):
- Analyze performance metrics and user feedback
- Architect configuration improvements and training updates
- Refine and update support procedures based on experience
- Assess progress toward business objectives
Who Should Lead Ongoing Implementation
Leadership during the post-go-live period requires different skills than implementation leadership.
Post-Go-Live Leadership Profile:
Business Process Owner (Primary Leader): A senior manager who understands both the business requirements and system capabilities. This person bridges the gap between technical possibilities and business needs, making decisions about process changes and system evolution.
Technical System Administrator: Someone with deep Odoo technical knowledge who can diagnose issues and implement solutions. This role requires technical skills and the ability to communicate with non-technical users.
Change Management Champion: A person skilled in organizational psychology who can maintain user morale, address resistance, and reinforce adoption. This role is critical during the first 90 days when user confidence is fragile.
Key Leadership Responsibilities:
- Maintain system performance and user satisfaction
- Prioritize enhancement requests and system improvements
- Coordinate between business departments and technical resources
- Plan for system scaling and future business requirements
Odoo Performance Optimization After Implementation
Post-go-live optimization extends beyond fixing problems—it’s about improving system performance to match business needs.
Fixing Performance Issues After Implementation
2025 Performance Optimization Approach:
Based on best practices, teams use AI-driven monitoring tools and automated optimization techniques to maintain peak system performance.
Database optimization starts with indexing for accessed data—think of it as creating shortcuts to the information you need. You’ll want to archive or delete unused historical records that slow down queries (nobody needs customer data from 1987), optimize complex queries and reduce joins that make your database work harder than it needs to, and implement automated maintenance procedures for health.
Infrastructure modernization means implementing caching layers and asynchronous task processing so users don’t wait for everything to happen in real-time. Set up a reverse proxy for SSL termination and load balancing to distribute the work, use containerization and auto-scaling for peak load management, and monitor resource utilization trends to predict scaling needs before you hit the wall.
Application-level optimization focuses on task queues for UI responsiveness during peak hours (because nothing frustrates users like waiting), optimized workflows that minimize database calls, custom module design that follows Odoo best practices instead of reinventing the wheel, and performance profiling to identify bottlenecks before they become emergencies.
Professional Optimization Tools:
- 🔧 Database Maintenance - Automated PostgreSQL optimization
- 📊 Weekly Maintenance - Regular system maintenance automation
- 🛡️ Database Corruption Detector - Proactive issue detection
Scaling Odoo After Implementation
As your business grows, your Odoo system needs to scale without disrupting operations.
Scaling Strategies for 2025:
Horizontal scaling is about adding servers to handle the load. You’ll implement multi-server deployments with load balancing to distribute the work, set up database read replicas for reporting and analytics so your reports don’t slow down your operations, dedicate servers for functions like backup, testing, and development (because production shouldn’t be your playground), and consider geographic distribution for operations.
Vertical scaling means making your existing servers more powerful. This includes memory optimization based on usage patterns rather than guessing, CPU upgrades driven by performance monitoring data instead of decisions, storage scaling with automated backup management, and network bandwidth optimization for remote users who shouldn’t feel like second-class citizens.
Performance monitoring and scaling triggers should warn you before problems become disasters. Set up automated alerts when response times exceed thresholds (because users notice slow systems before you do), implement capacity planning based on usage trend analysis so you’re not surprised by growth, scale before peak business periods rather than scrambling during Black Friday, and maintain real-time monitoring of critical business processes because some things can’t wait until tomorrow.
Database Maintenance Best Practices
PostgreSQL database health impacts Odoo performance and user satisfaction.
Automated Maintenance Procedures:
Daily maintenance requires automation because nobody wants to babysit databases. Set up automated backup verification and integrity checking (because backups that don’t work aren’t backups), performance monitoring and alert generation to catch problems, log analysis for error patterns and performance issues, and disk space monitoring with cleanup procedures so you don’t run out of space at 2 AM.
Weekly maintenance involves database vacuum and analyze operations to keep PostgreSQL running, index maintenance and optimization to prevent performance degradation, performance baseline updates and trend analysis to spot developing issues, and security patch assessment and planning because hackers don’t take weekends off.
Monthly maintenance means stepping back for the big picture. Conduct system health assessments to catch what daily monitoring misses, capacity planning and scaling recommendations based on usage trends, backup strategy review and optimization because requirements change, and security audit and compliance verification to ensure you’re meeting standards.
Monitoring and Analytics
Effective monitoring turns your Odoo system from a reactive tool into a predictive business intelligence platform.
Advanced Monitoring Implementation for 2025
Modern Monitoring Stack:
Real-time performance monitoring shows where implementations shine. Tools like Grafana paired with Prometheus give you system monitoring that tracks CPU, database, and application metrics in real-time. Automated alerting for critical thresholds—you want to know about problems before your users start complaining.
Error tracking and analysis using tools like Sentry transforms your approach to problem-solving. Instead of waiting for users to report issues, you get error tracking and performance monitoring that identifies problems before they impact operations. Debugging information enables resolution rather than hours of detective work.
Business intelligence integration elevates monitoring beyond technical metrics. Implementations track business process metrics alongside system performance—order processing times, user productivity metrics, and business KPI trends all flow through integrated dashboards. You see how technical performance translates to business outcomes.
Professional Monitoring Tools:
- 💗 Advanced Odoo Health Monitor - Comprehensive system monitoring
- 📈 Monthly Health Check - Regular performance assessment
- 🔍 Backup Quality Calculator - Backup system monitoring
Odoo Log Monitoring and Analysis
System logs contain warning signs for most issues, but only if you know how to interpret them.
Log Analysis Strategy:
Automated Log Processing:
- Real-time log parsing for error patterns and anomalies
- Trend analysis to identify developing performance issues
- Security monitoring for unauthorized access attempts
- Integration monitoring for third-party system failures
Performance Correlation:
- Link log events to performance degradation
- Identify user actions that trigger system stress
- Correlate error patterns with business process issues
- Track system resource usage patterns over time
Predictive Analytics:
- Use historical log data to predict system failures
- Identify capacity constraints before they impact users
- Plan maintenance windows based on usage patterns
- Optimize system configuration based on actual usage data
Advanced Reporting and Dashboard Customization
Post-implementation reporting needs evolve as business understanding of the system deepens.
Business Intelligence Evolution:
Executive Dashboards:
- Real-time KPI tracking with automated exception alerts
- Trend analysis and predictive analytics for strategic planning
- Cross-departmental performance metrics and collaboration indicators
- Mobile-optimized dashboards for leadership access anywhere
Operational Dashboards:
- Department-specific productivity metrics and workflow efficiency
- Real-time inventory and production status monitoring
- Customer service metrics and satisfaction tracking
- Financial performance and cash flow management
Advanced Analytics:
- Predictive modeling for inventory management and demand planning
- Customer behavior analysis and sales forecasting
- Cost center analysis and profitability optimization
- Risk assessment and compliance monitoring
Go-Live Success Metrics:
Monitor these critical indicators during your first 90 days:
- System Availability: >99.5% uptime during business hours
- Performance Baseline: Response times under 3 seconds for standard operations
- User Adoption: >95% of users using the system within 30 days
- Error Rate: <2% transaction failure rate across all modules
- Support Ticket Volume: Decreasing trend after first 2 weeks
- Business Process Efficiency: Meeting or exceeding pre-implementation baselines
Phase 6 Completion Milestones:
After 90 days post-go-live, verify that system performance meets baseline requirements, user satisfaction is high, business processes operate efficiently, and monitoring procedures are automated.
Remember: go-live is the beginning of your Odoo journey. The most successful implementations view the first 90 days as a period of learning and optimization, not a time to declare victory. Your system will evolve with your business, and your investment in proper support and optimization processes will pay dividends for years to come.
Common Implementation Mistakes to Avoid
Analysis of hundreds of Odoo implementations reveals patterns in both successes and expensive failures.
The brutal truth? Technical problems don’t cause most implementation failures—predictable, preventable mistakes that teams commit cause them.
The same mistakes that destroyed implementations in 2020 are happening in 2025, despite years of documented best practices and lessons learned.
People step into potholes that have warning signs.
When you understand these failure patterns, you can avoid them.
Companies that succeed don’t possess more intelligence or funding—they exercise discipline to avoid traps.
Common Odoo Implementation Mistakes to Avoid
Based on current industry data, over 70% of ERP implementations fail to meet their expected outcomes, with failure rates ranging from 50-75% depending on project scope. But these don’t represent random failures—they follow predictable patterns.
1. The “Requirements Gathering” Illusion
The Mistake: Teams confuse documenting current processes with understanding business requirements.
Most teams think they gather requirements when they document what people do today. Analysis shows companies spending months creating detailed process maps of inefficient workflows, then wondering why their new system doesn’t improve performance.
What happens is predictable and frustrating. Stakeholders describe their current workarounds instead of desired outcomes—they’ll spend an hour explaining how they reconcile invoices rather than saying “we want automated invoice matching.” Teams assume every existing process is necessary and valuable, even the ones that exist only because someone’s cousin’s friend said it was a good idea in 1995.
Requirements documents become novels that nobody reads or validates. Procedural details bury real business needs that miss the forest for the trees.
The Fix: Start with business outcomes, not current processes. Ask “What should success look like?” before asking “How do you do this today?”
2. The Over-Customization Death Spiral
The Mistake: Forcing Odoo to replicate every nuance of your system instead of adapting processes to leverage Odoo’s strengths.
Case studies document companies spending $200,000+ customizing Odoo to work exactly like their old system, then wondering why they didn’t just keep the old system. Over-customization is the #1 killer of Odoo implementations.
What happens is a slow-motion disaster. Teams justify expensive customizations to avoid minor process changes—they’ll spend $50,000 on custom code rather than ask users to click one extra button. Each customization creates dependencies that complicate future upgrades, turning simple updates into massive projects.
Maintenance costs compound exponentially with custom complexity—what starts as a $5,000 modification becomes a $50,000 ongoing maintenance burden. Users get frustrated with systems that work differently than standard Odoo, making training harder and support more expensive.
The Fix: Follow the 80/20 rule: adapt your processes to leverage 80% of Odoo’s standard functionality, then carefully customize only the 20% that provides genuine competitive advantage.
3. The “We Don’t Need Testing” Fallacy
The Mistake: Rushing to go-live without testing because “we’re behind schedule.”
Current Industry Reality: Teams that skip proper testing phases have a 75% higher failure rate than those that follow structured testing protocols.
What happens is Murphy’s Law in action. Teams discover critical issues during go-live when fixing them is most expensive and stressful—like finding out your inventory module can’t handle negative quantities during your busiest sales day. Users lose confidence in the system after encountering preventable problems, and once trust is broken, it’s incredibly hard to rebuild.
Simple bugs cascade into major business disruptions because systems are interconnected in ways you didn’t anticipate. Recovery from inadequate testing often takes longer than proper testing would have—you end up doing the testing you should have done, except now with angry users and lost productivity.
The Fix: Testing isn’t optional—it’s the most cost-effective insurance you can buy. Budget 20-25% of your implementation time for proper testing cycles.
4. The Partner Selection Gamble
The Mistake: Choosing implementation partners based on price or availability rather than Odoo expertise and cultural fit.
What Happens:
- General IT consultants without deep Odoo experience make configuration mistakes that compound over time
- Partners who lowball prices cut corners on planning, testing, and training
- Mismatched working styles create communication problems that derail projects
- Teams discover expertise gaps when they’re deep into implementation and changing partners is expensive
The Fix: Partner selection accounts for 50% of implementation success. Invest time in finding partners with demonstrated Odoo expertise, references from similar businesses, and communication styles that match your team.
⚠️ 68% of implementation failures trace back to ONE wrong decision
You just read about over-customization traps ($200K wasted), partner selection gambles (50% of success), and testing fallacies (75% higher failure rates). But here's what the data reveals: most of these disasters start with choosing the wrong hosting model.
Companies overestimate their technical capacity and choose self-hosting (then burn through budget on consultants). Or they underestimate their control needs and lock into managed hosting (then discover $15K migration costs when they need to switch). The wrong choice compounds every other mistake on this list.
Our Hosting Advisor prevents this by matching your ACTUAL technical capacity, budget constraints, and risk tolerance to the model with the lowest total cost of ownership. It's the one decision you can't afford to get wrong—make it based on data, not demos.
5. The Data Migration Disaster
The Mistake: Treating data migration as a simple file transfer instead of a complex data transformation process.
What Happens:
- Dirty source data creates duplicate records and broken relationships in Odoo
- Teams discover data quality issues after migration when fixing them is most difficult
- Historical reporting becomes unreliable due to migration errors
- Business intelligence suffers from inconsistent or incomplete data
The Fix: Data quality determines system quality. Invest in data cleaning and validation before migration, not after.
6. The Scope Creep Spiral
The Mistake: Adding modules, integrations, and customizations mid-project without understanding their cumulative impact.
What Happens:
- Projects that start with clear scope expand into sprawling, unmanageable initiatives
- Budgets explode as teams discover dependencies between added features
- Timelines extend indefinitely as complexity compounds
- Teams lose focus on core business objectives
The Fix: Scope discipline is project discipline. Document every scope change’s impact on timeline, budget, and complexity before approving it.
7. The Change Management Afterthought
The Mistake: Treating user training and change management as final steps rather than ongoing processes throughout implementation.
Current Reality: Projects with weak change management have user adoption rates below 60%, while those with strong change management exceed 95% adoption.
What Happens:
- Users resist systems they weren’t involved in designing
- Training feels like an imposition rather than empowerment
- People maintain shadow processes instead of fully adopting new workflows
- Management loses confidence as productivity initially decreases
The Fix: Change management starts on day one. Involve users in configuration decisions and build adoption momentum throughout the project.
8. The Technical Foundation Shortcut
The Mistake: Cutting corners on infrastructure, security, and performance optimization to save time or money upfront.
What Happens:
- Systems perform poorly under real-world loads, frustrating users
- Security vulnerabilities create compliance risks and potential breaches
- Inadequate backup and recovery procedures create business continuity risks
- Poor infrastructure choices limit scalability and future growth
The Fix: Technical shortcuts create long-term technical debt. Invest in proper infrastructure from the beginning.
9. The “Set It and Forget It” Mentality
The Mistake: Assuming implementation ends at go-live instead of planning for ongoing optimization and evolution.
What Happens:
- Systems stagnate while business requirements evolve
- Performance degrades over time without proactive maintenance
- Users develop workarounds for problems that should be fixed
- ROI plateaus instead of continuing to improve
The Fix: Implementation is the beginning of continuous improvement, not the end of system development.
10. The Communication Breakdown
The Mistake: Allowing communication gaps between technical teams, business stakeholders, and end users.
What Happens:
- Technical teams build systems that don’t match business expectations
- Business requirements get lost in translation during development
- End users feel excluded from decisions that affect their daily work
- Projects drift away from original objectives without anyone noticing
The Fix: Over-communicate rather than under-communicate. Regular stakeholder updates and feedback loops prevent expensive misunderstandings.
Recovery Strategies
When implementations go wrong, quick recognition and systematic recovery can often save projects that appear doomed.
Recognizing Implementation Failure
Early Warning Signs:
- User adoption rates below 70% after 60 days
- Increasing support ticket volume instead of decreasing trends
- Key stakeholders expressing serious concerns about system functionality
- Business processes taking longer than before implementation
- Teams maintaining shadow systems “just in case”
Critical Decision Points:
- 30 Days Post-Go-Live: If major functionality isn’t working, immediate intervention is required
- 60 Days Post-Go-Live: If user adoption hasn’t reached 85%, the implementation strategy needs revision
- 90 Days Post-Go-Live: If business metrics haven’t improved, fundamental changes are necessary
When to Pivot Your Approach
Indicators That Require Strategic Pivots:
Technical pivot scenarios indicate fundamental problems with your implementation approach. You’ll know it’s time to pivot when core modules consistently perform below acceptable standards despite optimization efforts, integration failures create ongoing business disruption that affects daily operations.
Customizations require more maintenance effort than the business value they provide (you’re spending more fixing than benefiting), or security and compliance issues emerge that can’t be resolved within your current architecture.
Business process pivot scenarios focus on the human and operational side. Consider pivoting when user workflows consistently require workarounds to accomplish basic tasks (if people are fighting the system daily, something’s wrong), business metrics show decreased efficiency compared to pre-implementation (you’re going backwards).
Change management efforts aren’t improving user adoption or satisfaction despite sustained effort, or stakeholder confidence in the project has been fundamentally undermined to the point where political support is gone.
Recovery Strategy Framework:
Phase 1: Immediate Stabilization (Week 1-2) is about stopping the bleeding. You need to identify and fix critical issues affecting daily operations first—people need to be able to work. Focus on restoring user confidence through quick wins and visible improvements, because morale matters more than perfect solutions right now.
Establish clear communication channels with all stakeholders so everyone knows what’s happening and when, and document all known issues while prioritizing them by business impact rather than technical complexity.
Phase 2: Root Cause Analysis (Week 3-4) digs deeper into why things went wrong. Conduct a thorough analysis of implementation decisions and outcomes without assigning blame—you’re looking for patterns, not scapegoats. Interview key users to understand specific pain points and requirements that may have been missed or misunderstood.
Evaluate your technical architecture and identify fundamental limitations that can’t be fixed with band-aids. Honestly assess team capabilities and partnership effectiveness to understand whether you have the right people in the right roles.
Phase 3: Strategic Recovery Planning (Week 5-6) is where you decide the path forward. Develop a comprehensive recovery plan with realistic timelines and budgets based on what you’ve learned. Make the hard decision whether to remediate your current implementation or restart with lessons learned—sometimes starting over is faster than fixing what’s broken.
Secure necessary resources and stakeholder commitment for recovery efforts, because half-measures won’t work. Plan your communication strategy to maintain momentum during recovery, because people need to believe this will get better.
Professional Recovery Tools:
- 🔄 Intelligent Rollback System - Basic rollback with optional data preservation
- 🚨 Emergency Recovery System - Complete disaster recovery toolkit
- 🛡️ Database Corruption Detector - Identify and assess data integrity issues
Technical Troubleshooting
When technical issues arise, systematic troubleshooting prevents small problems from becoming implementation disasters.
Module Installation and Conflict Resolution
Common Module Issues (2025 Update):
Based on current community data, over 60% of technical errors stem from dependency management and module conflicts.
Dependencies and conflicts create module problems. You’ll encounter missing or incompatible Python libraries required for module functionality (the dreaded “module not found” error), version mismatches between modules and the Odoo core platform (after upgrades).
Incorrect manifest.py configurations cause installation failures, and external ID conflicts when modules define overlapping data records that confuse the system about which version to use.
Resolution Approach:
Enable debug mode for detailed error information:
URL: your-odoo.com/?debug=1
Check server logs for specific error messages:
tail -f /var/log/odoo/odoo-server.log
Verify module dependencies: Navigate to Settings > Technical > Database Structure > Models
Professional Diagnostic Tools:
- 🧩 Module Compatibility Scanner - Analyze module compatibility and conflicts
- 🔗 Dependency Analyzer - Resolve complex module dependencies
- ⚙️ Dependency Resolution Engine - Intelligent conflict resolution
Performance Problem Resolution
Common Performance Issues:
Database performance issues arise from slow queries caused by missing indexes on accessed fields (the database doesn’t know how to find your data).
Database bloat from accumulated transaction logs and historical data that nobody’s cleaning up, optimized queries with joins or subqueries that make the database work harder than needed, and PostgreSQL configuration for production workloads compound these problems.
Application performance problems include memory leaks in custom modules causing performance degradation over time.
Workflows that generate database operations (death by a thousand queries), configured caching that results in repeated operations, and integration bottlenecks with external systems that slow down everything else create additional performance drain.
Resolution strategy begins with using performance profiling tools to identify bottlenecks rather than guessing. Implement database maintenance procedures for optimization because performance degrades over time without care. Review and optimize custom code following Odoo best practices instead of reinventing wheels. And monitor resource utilization trends to predict scaling needs before you hit the wall.
Integration Error Troubleshooting
Common Integration Problems:
API connectivity problems include authentication failures due to expired tokens or changed credentials (discovered at the worst moment).
Network timeouts caused by latency or firewall configurations that nobody documented, rate limiting issues when making API calls (throttled), and data format mismatches between systems that expect different structures add complexity.
Data synchronization challenges encompass mapping errors when field structures don’t align between systems (what one system calls “customer_name” another calls “client_title”).
Timing issues when one system updates faster than others can sync, error handling problems when integration failures cascade across systems like dominoes, and monitoring gaps that allow failed synchronizations to go unnoticed until someone asks “where’s my data?”
Professional Integration Tools:
- 🌐 API Diagnostics Tool - Basic external API connectivity validation
- 📧 SMTP Configuration Tester - Email system integration validation
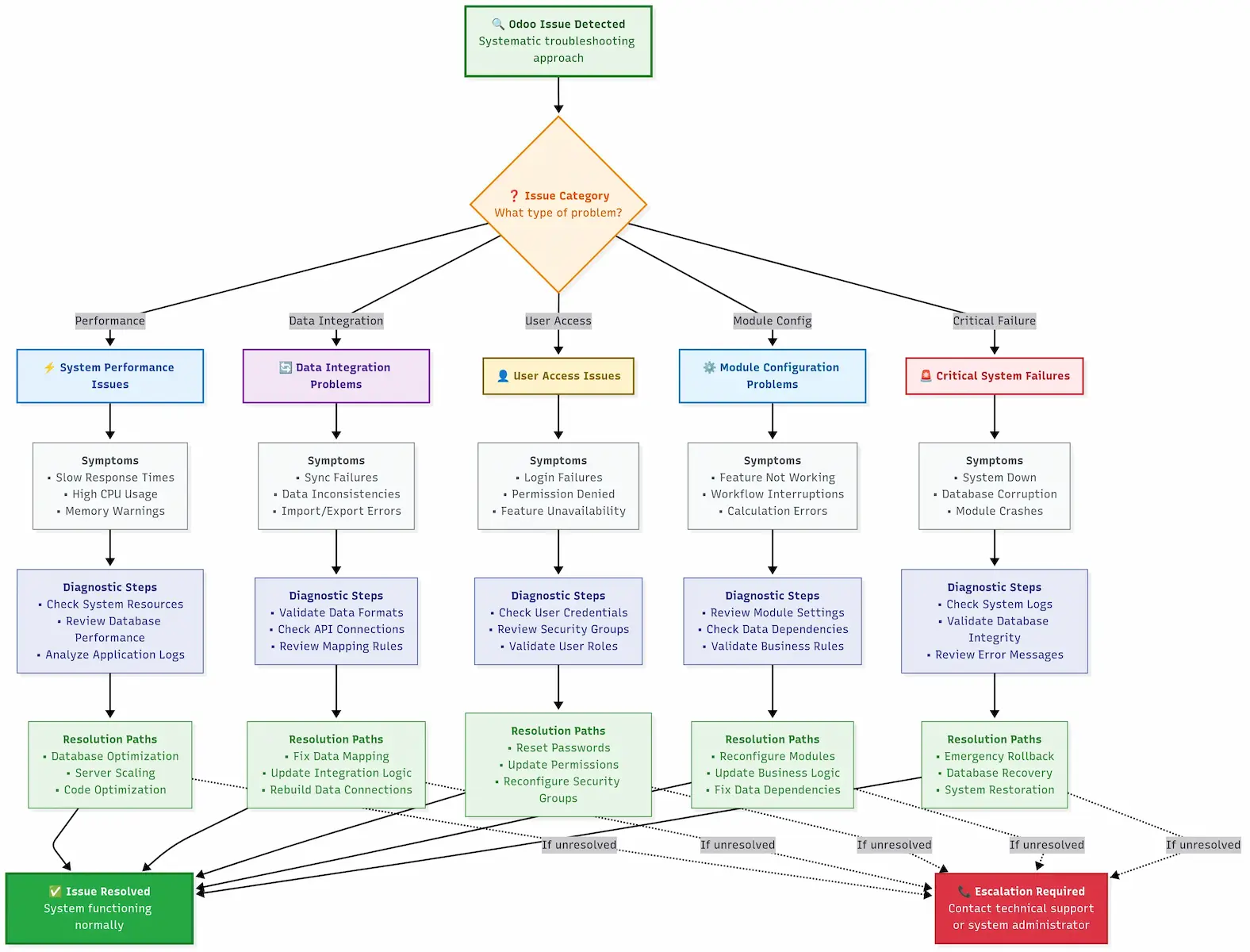 Systematic troubleshooting flowchart covering performance, integration, access, and data quality issues
Systematic troubleshooting flowchart covering performance, integration, access, and data quality issues
Implementation Risk Mitigation Checklist:
Before starting your Odoo implementation, verify that you define clear business objectives, you have a realistic timeline, you select an experienced implementation partner, and you properly size technical infrastructure.
Remember: implementation mistakes cost heavily to fix after go-live, but they’re preventable with planning and execution. The most successful Odoo implementations aren’t the ones that never encounter problems—they’re the ones that anticipate problems and have systems in place to resolve them.
Partner Selection and Team Building
The reality about Odoo implementations: partner selection determines 50% of your implementation success. Analysis reveals perfect teams failing because they chose partners based on price rather than capability.
Mediocre implementations succeed when the right partner manages the process.
After analyzing hundreds of implementations, the pattern is clear:
Companies that invest time in selecting the right partners and building strong internal capabilities achieve success rates exceeding 90%. Those that rush into partnerships or neglect internal team development experience failure rates above 60%.
The challenge: partner selection occurs when you understand the least about what you need.
It’s like hiring a surgeon before you know what operation you require.
Most companies make partner decisions based on demos and proposals, then discover six months later that they’ve committed to a relationship that can’t deliver what they need.
But when you approach partner selection and team building systematically, something transforms: implementation becomes a collaborative process that leverages the best of both worlds—external expertise and internal knowledge.
💡 Before hiring a partner or going solo: The partner vs. self-hosting decision depends entirely on your team’s REAL technical capacity—not what you think they can handle, but what they can actually sustain. Our free Hosting Advisor assesses whether your team has the Linux/PostgreSQL expertise and available time for self-hosting, or if managed hosting/partners are actually the lower-cost option when you factor in staff time. Brutally honest answers reveal your optimal path. Take the 2-minute capacity assessment →
How to Choose Odoo Implementation Partner
The implementation partner you choose shapes every aspect of your project, from timeline and budget to user adoption and long-term success. This isn’t a decision you can afford to get wrong.
How to Choose the Right Odoo Implementation Partner
The Partner Selection Framework:
Partner selection isn’t about finding the “best” partner—it’s about discovering the partner that’s best for your situation, industry, and organizational culture.
1. Official Partnership Status and Certification (25% Weight)
Odoo categorizes partners Ready, Silver, and Gold based on three criteria:
New Odoo Enterprise users sold over the last 12 months (they’re selling, not just talking), number of certified employees on the 3 latest Odoo versions (they keep their skills current), and customer retention rates with minimums of 70% for Silver and 80% for Gold (their clients stick around).
What each level means:
Ready Partners can deploy basic Odoo functionality with standard configurations—they’re fine for straightforward deployments.
Silver Partners can manage complex solutions with moderate customizations and have proven track records.
Gold Partners are proven developers with experience in complex platform implementations—these are the partners you want for challenging projects.
Why This Matters: According to 2025 data, 74% of ERP implementation failures occur because partners lack understanding of operational nuances. Official certification doesn’t guarantee success, but it reduces risk.
2. Industry-Specific Experience (30% Weight)
The Industry Expertise Test: Challenge potential partners to describe three implementations in your industry that went wrong and how they fixed them. Generic answers reveal surface-level experience.
Questions that reveal expertise: Ask them “What challenges does our industry face that others don’t?” and analyze their answers, not generic responses. Request “Show us a demo using data and workflows from our industry”—if they can’t do this, they haven’t worked in your space. Inquire about “What industry-specific compliance requirements will affect our implementation?” because regulations matter. And find out “Which of your team members has worked with companies like ours?” because you want to work with people who understand your world.
Red Flag: Partners who accept every request without questioning complexity or viability lack industry understanding.
3. Technical Expertise and Methodology (20% Weight)
Core technical requirements include proficiency in Python and JavaScript for Odoo development and customization (because that’s what Odoo is built on), experience with PostgreSQL optimization and performance tuning (your database will make or break performance), understanding of web development frameworks and API integrations (everything connects to everything these days), and knowledge of deployment practices like Docker, cloud platforms, and CI/CD (because manual deployment is so 2015).
Methodology assessment means probing their processes. Do they follow a documented implementation methodology, or do they improvise? How do they manage scope changes and project risks when (not if) they arise? What tools do they employ for project management and communication, and are they tools you can work with? How do they tackle testing and quality assurance—do they have a process, or do they hope for the best?
4. Communication and Cultural Fit (15% Weight)
The communication test occurs during the selection process itself. Monitor their response time to emails and questions (if they’re slow now, they’ll be slower later).
Clarity of explanations for stakeholders (can they speak human, not just geek?), willingness to admit limitations and suggest alternatives (honesty over salesmanship), and alignment with your company’s working style and values.
Cultural fit indicators reveal themselves through behavior, not promises. Do they ask questions about your business goals beyond requirements? How do they handle disagreements or pushback on recommendations—with defensiveness or discussion? Are they comfortable working with your existing team and processes, or do they insist on doing everything their way? Do they demonstrate understanding of your company’s decision-making style, or do they seem frustrated by how you operate?
5. Post-Implementation Support Strategy (10% Weight)
Support structure questions probe the heart of partnership viability. What support encompasses the implementation contract, and what costs extra? How do they handle urgent issues and system failures—do they have escalation procedures, or do you get voicemail? What training and knowledge transfer do they deliver to build your internal capabilities? And how do they manage software updates and version upgrades without disrupting your business?
Long-term Relationship Assessment:
- Do they have clients who’ve worked with them for multiple years?
- How do they handle contract renewals and ongoing relationships?
- What’s their strategy for keeping clients current with Odoo developments?
Evaluating Implementation Vendors and Consultants
The Vendor Evaluation Process:
Phase 1: Initial Screening (Week 1)
- Review official partner status and certifications
- Verify industry experience and client references
- Assess technical capabilities and methodology documentation
- Evaluate communication quality and responsiveness
Phase 2: Deep Dive Assessment (Week 2-3)
- Conduct detailed interviews with proposed project teams
- Review case studies and implementation examples from your industry
- Assess project management tools and communication processes
- Verify support structure and ongoing relationship management
Phase 3: Proof of Concept (Week 4)
- Request a limited proof of concept using your actual data
- Evaluate their approach to configuration and customization decisions
- Assess team dynamics and collaboration style
- Test their problem-solving approach when issues arise
Vendor Comparison Framework:
Partner Evaluation Scorecard:
- Technical Capability: ___/25 points
- Industry Experience: ___/30 points
- Methodology & Process: ___/20 points
- Communication & Culture: ___/15 points
- Support & Relationship: ___/10 points
Total Score: ___/100 points
Decision Criteria:
- Score 85+: Excellent partner candidate, proceed with detailed negotiations
- Score 70-84: Good partner with some gaps, address specific concerns
- Score <70: High risk, consider other options unless you can resolve gaps
Building Internal Capabilities
Your internal team capabilities determine how effectively you can work with external partners and maintain the system long-term.
Odoo Implementation Team Structure Requirements
The Core Internal Team:
1. Executive Sponsor (10% time commitment)
- Senior leadership with authority to make strategic decisions
- Responsible for removing organizational barriers and securing resources
- Final arbiter for scope changes and major configuration decisions
- Champion for change management and user adoption initiatives
2. Project Leader/Business Process Owner (50% time commitment)
- Deep understanding of current business processes and desired outcomes
- Authority to make day-to-day configuration and process decisions
- Primary liaison with implementation partner and internal stakeholders
- Responsible for user acceptance testing and training coordination
3. Technical Champion (30% time commitment)
- IT professional with database and systems administration experience
- Responsible for infrastructure setup and ongoing technical maintenance
- Point person for integration planning and technical troubleshooting
- Future system administrator for ongoing configuration and updates
4. Department Representatives (20% time commitment each)
- Key users from Finance, Operations, Sales, and HR departments
- Subject matter experts for their respective business areas
- Responsible for department-specific requirements and user training
- Champions for change management within their teams
5. Data Steward (40% time commitment during migration phases)
- Expert in current data systems and data quality issues
- Responsible for data cleanup, mapping, and migration validation
- Point person for ongoing data governance and quality assurance
- Knowledgeable about compliance and regulatory data requirements
Who Should Lead Your Odoo Implementation
The Implementation Leadership Decision:
The person who spearheads your implementation will determine its success. This isn’t a role you can assign based on availability—it requires skills and organizational positioning.
Ideal Leader Profile:
Business Process Expert with Technical Aptitude: Someone who understands your business operations but can also master concepts and communicate with developers.
Organizational Credibility: Must command respect across departments and authority to drive decisions and resolve conflicts.
Project Management Skills: Experience orchestrating complex projects with external vendors and internal stakeholders.
Change Management Capability: Ability to overcome organizational resistance and build enthusiasm for new processes.
Common Leadership Mistakes:
Mistake 1: Assigning Based on Availability Selecting someone because they have time rather than the right skills and authority.
Mistake 2: IT-Only Leadership Having IT lead without business process involvement produces sound but business-poor implementations.
Mistake 3: Committee Leadership Attempting to lead by committee without decision-making authority creates delays and scope creep.
Hiring and Training Internal Champions
The Internal Champion Strategy:
Internal champions guarantee your success. They eliminate dependency on external consultants and ensure institutional knowledge remains within your organization.
Champion Selection Criteria:
Technical Aptitude:
- Comfortable mastering software and troubleshooting problems
- Ability to grasp relationships between system modules
- Interest in process improvement and optimization
Organizational Influence:
- Respected by peers and trusted by management
- Teachers who excel at helping others learn
- Attitude toward change and technology
Department Representation:
- Mastery of their department’s processes and challenges
- Authority to make configuration decisions for their area
- Ability to deliver training and support to their teams
Champion Development Program:
Phase 1: Foundation Training (Week 1-2)
- Odoo navigation and functionality
- Understanding of data relationships and system architecture
- Basic configuration and customization capabilities
Phase 2: Advanced Skills (Week 3-4)
- Module features and configurations
- Reporting and dashboard creation
- Integration understanding and troubleshooting
Phase 3: Teaching Skills (Week 5-6)
- Learning principles and training techniques
- Creating training materials and job aids
- Change management and user adoption strategies
Working with Partners
You must orchestrate partner relationships through expectations, communication, and performance management.
Finding and Working with Odoo Certified Partners
The Official Partner Network:
Odoo maintains an official partner directory, but partners vary in quality. The certification levels provide guidance, but your specific needs require deeper evaluation.
Finding partners begins with knowing where to look. The Odoo Official Partner Directory lets you filter by industry, location, and certification level to create an initial list—it’s your starting point, not your ending point. Industry networks harbor Odoo partners who focus on sectors and understand your challenges. Referrals from businesses deliver honest feedback—question companies in your industry about their implementation experiences and partner recommendations. And Odoo community events provide opportunities to see partner presentations that reveal expertise levels and communication skills.
Managing Partner Relationships and Setting Expectations
The Partner Relationship Framework:
1. Contract Structure and Expectations
Scope definition prevents scope creep from killing projects. You need module and functionality specifications that everyone endorses.
Integration requirements and specifications that account for your existing systems, training deliverables and knowledge transfer requirements that build your internal capabilities, and support levels with response time commitments that get met.
Timeline and milestone management builds accountability through structure. Create progress reports with deliverable tracking (no vague “we’re making progress” updates).
Stakeholder reviews with scope and timeline assessment, relationship reviews with performance evaluation, and change management procedures with impact assessment requirements before anything gets approved.
2. Communication Protocols
Communication schedule maintains everyone informed and engaged. Schedule standups during development phases to catch issues early.
Progress reviews with stakeholders to maintain alignment, reviews with executive sponsors to ensure business objectives stay front and center, and relationship and performance evaluations to address any partnership issues.
Escalation procedures address the problems. Establish a definition of what constitutes an escalation issue (not every question needs executive attention).
Set response time requirements for severity levels, define authority levels for decision-making at each escalation tier, and create documentation requirements for escalated issues so lessons get learned.
3. Performance Management
Key performance indicators track what matters:
Timeline adherence and milestone completion rates (are we on track?), budget variance and scope change management (are we spending what we planned?), user satisfaction scores and adoption metrics (do people like and use the system?), and post-implementation system performance and stability (does it work?).
Quality gates ensure standards are met before moving forward. Implement configuration review and approval processes so nothing goes live without review, testing completion and sign-off requirements that verify everything works, training completion and competency verification to ensure users can operate the system, and go-live readiness assessment with approval criteria that must be met.
Relationship health monitoring stops partnership problems from festering. Schedule feedback sessions with stakeholders to surface issues early.
Create feedback channels for communication when hierarchy gets in the way, identify and resolve relationship issues before they damage the project, and plan improvement for partnership effectiveness based on what you’re learning.
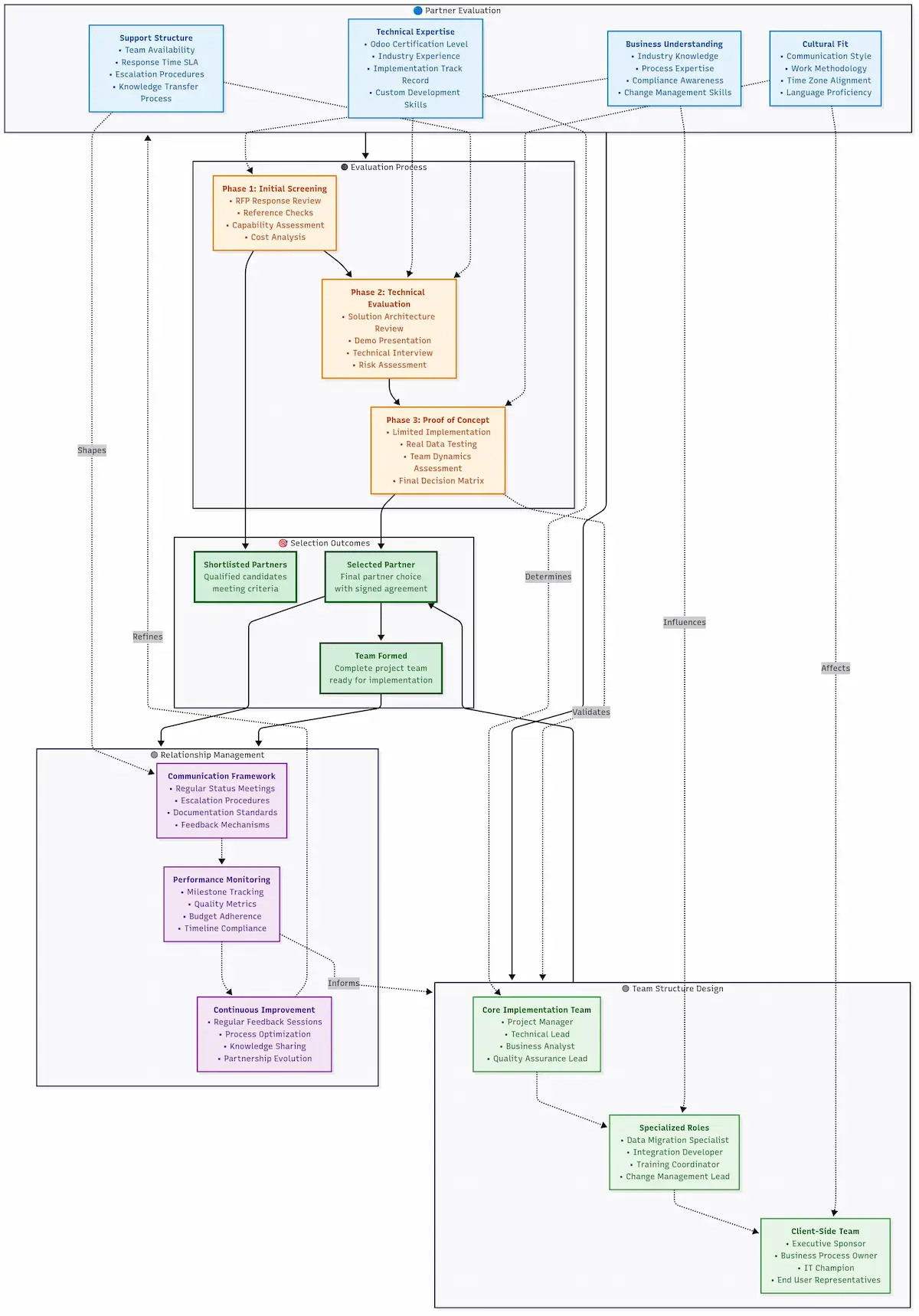 Strategic partner selection framework with evaluation criteria, team structure design, and relationship management
Strategic partner selection framework with evaluation criteria, team structure design, and relationship management
Partner Selection Success Checklist:
Before finalizing your implementation partner, verify their certification, industry experience, capabilities, and cultural fit.
For internal team readiness, ensure you have committed executive sponsorship, identified project leadership, and prepared champions for system administration.
Remember: the cheapest partner rarely delivers the best value, and the expensive isn’t always the best choice. Focus on discovering partners who understand your business, communicate effectively, and demonstrate commitment to your success. Your implementation partner becomes an extension of your team—choose accordingly.
Project Management and Methodology
The truth about Odoo implementations: timing and budget are the elements that dictate whether your methodology succeeds. A project achieves success if it’s delivered on time and on budget—everything else is secondary.
Analysis of hundreds of implementations shows that methodology isn’t about following a process—it’s about having a framework that adapts to challenges while maintaining focus on delivery.
The most successful implementations aren’t the ones that follow textbook methodologies; they’re the ones that use frameworks as starting points and adapt when reality intervenes.
The challenge: teams treat methodology like a religion rather than a tool. They spend weeks perfecting project plans that become obsolete the moment implementation starts. What distinguishes successful implementations is having a methodology that’s robust to handle uncertainty while being flexible to adapt when information emerges.
When you merge methodology with project management, something transforms: implementation becomes predictable, manageable, and more likely to deliver the business results you’re expecting.
Odoo Implementation Methodology Best Practices
The methodology you select determines how you’ll navigate the journey from business requirements to working system. This isn’t about selecting a framework—it’s about crafting an approach that maximizes success probability while minimizing risk.
Odoo Implementation Methodology Best Practices
The 2025 Implementation Framework:
Odoo implementations employ a methodology that combines project management with agile principles and validation. This isn’t the waterfall approach of the past or the chaos of agile—it’s a structured, adaptive methodology crafted for ERP implementations.
Core Methodology Principles:
1. Business Configuration Begin with business outcomes, not features. Every configuration decision should map to a business improvement or requirement.
2. Validation Verify functionality with users and data rather than waiting for testing phases.
3. Risk Prioritization Tackle risk elements first when they’re easiest to change, not when they become urgent.
4. Stakeholder Engagement Maintain involvement from business stakeholders throughout implementation, not just during requirements gathering.
How to Implement Odoo Step by Step
The 8-Phase Implementation Process:
Phase 1: Project Kick-off & Foundation (Week 1-2)
The project kick-off generates buy-in within your organization, manages expectations, and builds a foundation. This phase determines whether your implementation succeeds or fails.
Key activities focus on getting everyone aligned before you start building anything. You’ll need executive stakeholder alignment and commitment validation (make sure the people signing checks are committed), implementation team formation and role assignment (so everyone knows who does what), communication plan establishment and escalation procedures (because things will go wrong), success criteria definition and measurement framework (so you know when you’re done), and risk assessment and mitigation planning (because problems are easier to prevent than fix).
Deliverables include a project charter with scope and boundaries (so you can say “no” to scope creep), a stakeholder responsibility matrix that spells out who’s responsible for what, communication protocols and meeting schedules that get followed, success metrics and acceptance criteria that everyone agrees on, and a risk register with mitigation strategies for the problems you can see coming.
Phase 2: Requirements Gathering & Business Analysis (Week 3-5)
This phase is about understanding current state and desired future state, not documenting every process.
Key activities involve understanding where you are and where you want to go. Start with current state assessment and process mapping (but don’t get lost in documenting broken processes), move to future state visioning with business stakeholders (focus on outcomes, not features), conduct gap analysis between current and desired states, make module selections based on business requirements rather than what looks cool in demos, and identify integration requirements early before they become surprises.
Deliverables include a Business Requirements Document that people will read, process maps showing both current and future states, a module selection matrix with justification for each choice, integration requirements specification that covers your systems, and a project timeline and budget that’s more than wishful thinking.
Phase 3: Solution Design & Architecture (Week 6-8)
Transform business requirements into technical specifications and implementation roadmap.
Key Activities:
- System architecture design and infrastructure planning
- Workflow configuration planning with approval processes
- User role and permission structure design
- Data migration strategy and mapping design
- Customization vs. configuration decision framework
Deliverables:
- Architecture document
- Workflow design specifications
- User access and security matrix
- Data migration plan with field mappings
- Configuration vs. customization recommendations
Phase 4: System Setup & Configuration (Week 9-12)
The technical execution phase where requirements become working system functionality.
Key Activities:
- Odoo environment setup (development, staging, production)
- Core module installation and basic configuration
- Workflow configuration with business rule implementation
- User account creation and permission assignment
- Integration setup and initial testing
Deliverables:
- Configured Odoo environment with core functionality
- Documented configuration settings and rationale
- User accounts with appropriate access levels
- Integration frameworks with basic connectivity
- Configuration testing results and issues log
Phase 5: Data Migration & System Integration (Week 13-16)
Transform and transfer business data while establishing system connections.
Key Activities:
- Data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL)
- Data quality validation and cleanup procedures
- Integration testing with external systems
- Performance testing under realistic data loads
- Backup and recovery procedure validation
Deliverables:
- Migrated data with quality validation reports
- Working integrations with external systems
- Performance benchmarks and optimization recommendations
- Backup and disaster recovery procedures
- Data governance policies and procedures
Phase 6: Testing & Validation (Week 17-19)
Testing to ensure system meets business requirements and performance standards.
Key Activities:
- Unit testing of modules and functions
- Integration testing across modules and systems
- User acceptance testing with business scenarios
- Performance testing under user loads
- Security testing and vulnerability assessment
Deliverables:
- Test cases with execution results
- User acceptance testing sign-off documents
- Performance benchmarks and optimization plans
- Security assessment report with remediation plans
- Go-live readiness assessment
Phase 7: Training & Change Management (Week 20-22)
Prepare your organization for system adoption and change.
Key Activities:
- Role-based training program execution
- Train-the-trainer sessions for internal champions
- Change management activities and adoption support
- Documentation creation (user guides, procedures)
- Support structure establishment and testing
Deliverables:
- Trained user base with competency verification
- Internal champion certification and capabilities
- User documentation and job aids
- Support procedures and escalation protocols
- Change management success metrics baseline
Phase 8: Go-Live & Post-Implementation Support (Week 23-26)
Deploy the system and provide support during the adoption period.
Key Activities:
- Production cutover with business disruption
- User support during adoption period
- Issue tracking and resolution procedures
- Performance monitoring and optimization
- Success metrics tracking and reporting
Deliverables:
- Production deployment with user adoption
- Issue resolution log with response time tracking
- Performance monitoring reports and trends
- Success metrics dashboard with KPI tracking
- Post-implementation optimization recommendations
Phased Implementation Approach
The Strategic Phasing Decision:
Not all businesses should implement Odoo in a single “big bang” approach. Phased implementation reduces risk, enables learning, and provides value.
When to Use Phased Implementation:
Large Organizations (50+ users): Phased approach reduces change management complexity and allows for course correction between phases.
Complex Business Processes: Multiple interconnected workflows benefit from phase-by-phase validation and refinement.
Limited Internal Resources: Smaller teams can focus on one area at a time, building expertise.
High-Risk Implementations: Complex customizations or integrations benefit from proof-of-concept validation before deployment.
Phased Implementation Strategies:
Strategy 1: Functional Phasing Implement by business function (Finance → Sales → Operations → HR)
Advantages:
- Clear ownership and accountability per phase
- Focused training and change management
- Natural progression from core to supporting functions
Timeline: 6-12 months total with 2-3 month phases
Strategy 2: Geographic Phasing Implement by location or business unit
Advantages:
- Pilot and learning opportunity
- Reduced risk to business operations
- Ability to refine approach based on results
Timeline: 4-8 months total with 1-2 month phases per location
Strategy 3: Complexity Phasing Start with standard functionality, add complex features later
Advantages:
- Wins and value demonstration
- User adaptation to system complexity
- Lower implementation risk
Timeline: 3-6 months for core, additional phases as needed
Project Plan Template Framework
The Dynamic Project Plan:
Project plans become obsolete in ERP implementations. Use a framework that adapts to changing requirements while maintaining structure.
Planning Elements:
1. Milestone Structure
- Milestones every 2-4 weeks
- Go/No-go decision points at each milestone
- Deliverables and acceptance criteria
- Stakeholder approval requirements
2. Resource Allocation
- Team time commitments by phase
- Partner resource requirements
- Budget allocation with contingency reserves
- Path dependencies and constraints
3. Communication Framework
- Progress reports with stakeholder distribution
- Steering committee reviews
- Alignment assessments
- Ad-hoc escalation procedures for issues
4. Quality Gates
- Configuration review and approval checkpoints
- Testing completion and sign-off requirements
- Training validation and competency verification
- Go-live readiness assessment criteria
Risk Management
Risk management in Odoo implementations isn’t about avoiding risks—it’s about identifying, quantifying, and managing risks rather than reacting.
Implementation Risk Assessment Framework
The Risk Categorization Matrix:
High-Probability, High-Impact Risks:
- Stakeholder engagement and buy-in
- Data quality in source systems
- Scope creep without change management
- Integration complexity with systems
High-Probability, Low-Impact Risks:
- Minor configuration changes during implementation
- Training schedule adjustments for user availability
- Performance tuning requirements during testing
- Documentation updates based on configuration changes
Low-Probability, High-Impact Risks:
- Key stakeholder departure during implementation
- Major business process changes during implementation
- Technical infrastructure failures during go-live
- Regulatory changes affecting system requirements
Low-Probability, Low-Impact Risks:
- Minor software bugs in standard Odoo functionality
- Temporary network connectivity issues during implementation
- Small adjustments to reporting formats
- Minor user interface customization requests
Risk Management Strategies
Risk Mitigation:
Stakeholder Risk Management:
- Secure executive sponsorship with commitment levels
- Identify and engage resistors in the process
- Establish escalation paths for decision-making
- Create stakeholder communication plan with touchpoints
Technical Risk Management:
- Conduct proof-of-concept for integrations
- Establish development, staging, and production environments
- Implement backup and recovery procedures
- Plan for performance testing under load conditions
Data Risk Management:
- Conduct data quality assessment before migration planning
- Implement data cleansing procedures in the process
- Plan for migration test cycles with validation
- Establish data governance procedures for quality
Project Risk Management:
- Build 20% schedule buffer for issues
- Establish scope change management procedures
- Plan for person risk with knowledge transfer
- Create communication protocols for issue resolution
Contingency Planning
The Emergency Response Framework:
Issue Severity Levels:
Severity 1: Implementation-Stopping Issues
- Core functionality non-functional
- Data corruption or loss during migration
- System performance failure
- Security breach or compliance violation
Response Time: Immediate (within 2 hours) Escalation: Direct to executive sponsors and partner leadership
Severity 2: Significant Functionality Issues
- Major module not working as configured
- Integration failures affecting business processes
- Performance degradation impacting user productivity
- Training delays affecting go-live timeline
Response Time: Within 24 hours Escalation: Project management team and department heads
Severity 3: Minor Functionality Issues
- Configuration adjustments needed for user workflows
- Reporting format adjustments or corrections
- Training material updates or clarifications
- Documentation corrections or enhancements
Response Time: Within 72 hours Escalation: Internal project team with partner support
Milestone Tracking
Milestone tracking provides warning of issues while maintaining focus on business value delivery.
Implementation Milestone Framework
The Value Milestone Structure:
Business Value Milestones:
- Requirements validation and stakeholder sign-off
- Core functionality demonstration with data
- User acceptance testing completion with adoption metrics
- Go-live success with performance benchmarks met
Technical Delivery Milestones:
- Environment setup and configuration completion
- Data migration success with quality validation
- Integration testing completion with performance validation
- Security and compliance verification with approval
Organizational Readiness Milestones:
- Team formation and responsibility assignment
- Training completion with competency verification
- Change management activities with adoption metrics
- Support structure activation with escalation testing
Progress Monitoring and Reporting
The Dashboard Approach:
**Executive Dashboard (Updates):”
- Overall project status (on-track, at-risk, off-track)
- Budget variance and timeline status
- Key milestone completion rates
- User adoption and satisfaction metrics
Project Management Dashboard (Updates):
- Task completion rates by phase and team member
- Issue identification and resolution tracking
- Resource utilization and availability status
- Risk register updates with mitigation progress
Operational Dashboard (Updates During Phases):
- Task completion and obstacle identification
- Metrics for deliverables and testing
- Stakeholder engagement and feedback tracking
- Technical performance and issue resolution
Adapting to Changes and Delays
The Response Framework:
Change Classification:
- Scope Changes: New requirements or functionality requests
- Timeline Changes: Delays due to complexity or resource constraints
- Resource Changes: Team member availability or skill adjustments
- Priority Changes: Business priority shifts requiring re-sequencing
Response Strategies:
Scope Change Management:
- Impact assessment for timeline, budget, and resource requirements
- Stakeholder approval process with clear decision-making authority
- Documentation updates and communication to all affected parties
- Implementation plan adjustments with risk reassessment
Timeline Recovery Options:
- Task execution where dependencies allow
- Resource augmentation for critical path activities
- Scope reduction or phasing to meet critical deadlines
- Quality gate adjustments with stakeholder approval
Resource Optimization:
- Cross-training to reduce single points of failure
- External resource augmentation for skills
- Task redistribution based on individual strengths and availability
- Knowledge transfer acceleration to build internal capabilities
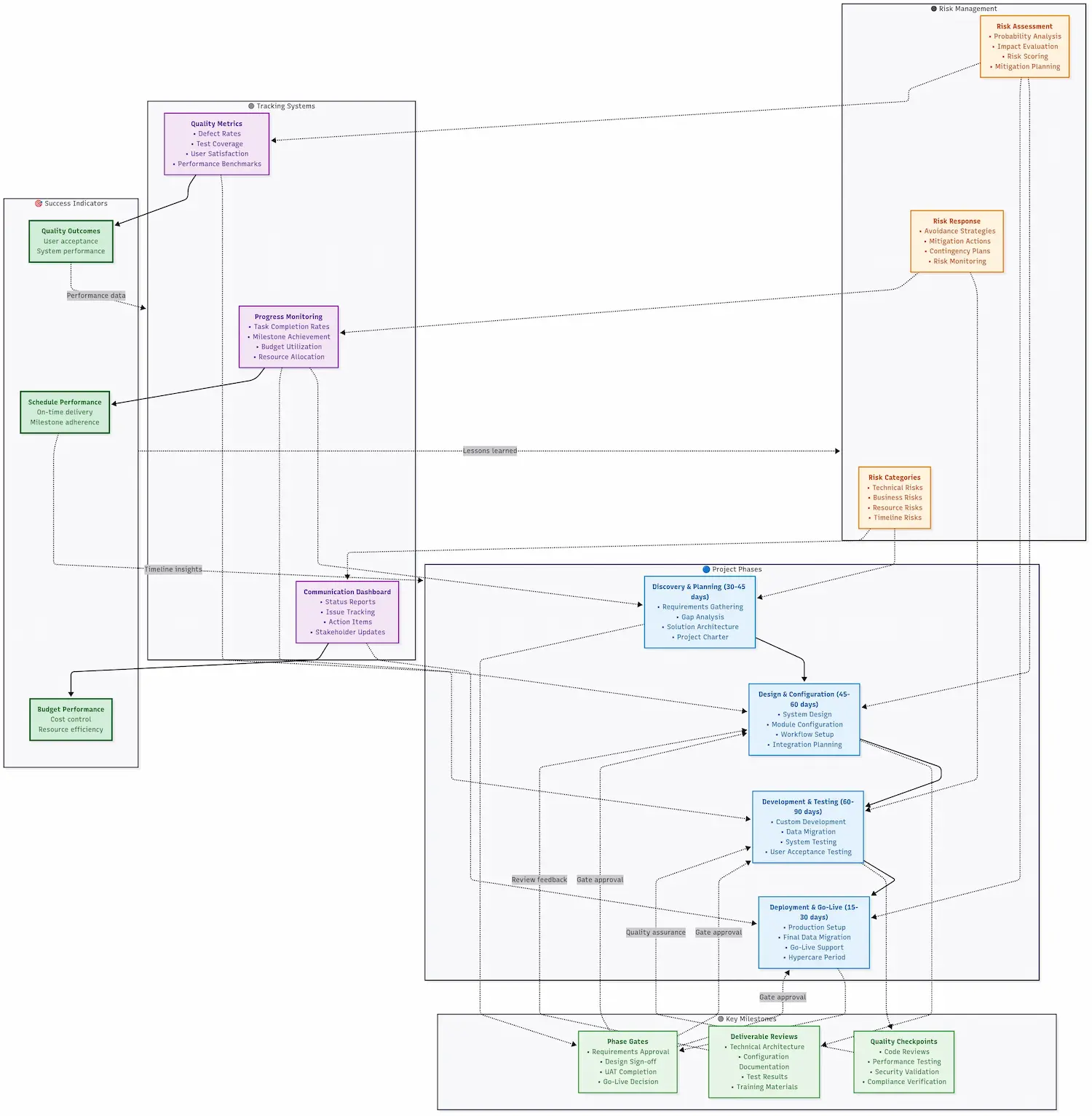 End-to-end project management framework showing phases, milestones, risk management, and tracking systems
End-to-end project management framework showing phases, milestones, risk management, and tracking systems
Implementation Success Checklist:
Before proceeding to the next phase, confirm that milestone deliverables are completed and approved, stakeholder sign-off is obtained, risk register is updated, and quality gates are met with documented evidence.
Remember: methodology serves as a framework, not a straitjacket. The implementations transform methodology to fit business reality while maintaining the discipline and structure needed for success. Your goal isn’t adherence to process—it’s delivering a working system that transforms business outcomes on time and on budget.
Alternative Solutions Comparison
The conversation consultants won’t have with you: Odoo isn’t the right solution for every business. Case studies reveal companies force-fitting Odoo into situations where other solutions would have served them.
Analysis exposes businesses abandoning systems because they didn’t understand what they were getting into.
Analysis of dozens of ERP implementations shows that the solution isn’t the popular one—it’s the one that matches your business reality, technical capabilities, and growth trajectory.
Sometimes that’s Odoo, sometimes it’s not.
The challenge: comparison resources are authored by vendors trying to sell you something, or by consultants who specialize in one platform.
You end up with biased information that drives you toward what the author makes money selling.
But when you understand the real strengths and limitations of different approaches, something transforms: you craft decisions based on what will work for your business, not what sounds good in a demo.
Odoo vs SAP vs NetSuite Implementation Comparison
Let’s examine the truths about Odoo that implementation guides skip over.
Honest Assessment of Odoo Limitations
The Complexity Ceiling Problem:
Odoo handles business processes, but it encounters walls when you need functionality.
Analysis reveals this pattern: companies select Odoo because it looks and affordable, then discover six months later that their business requirements exceed what Odoo can handle.
Enterprise-Scale Limitations:
Multi-Entity Operations: If your business requires multi-entity consolidation, intercompany transactions, or multi-currency consolidation, Odoo’s tools are limited.
You’ll find yourself wrestling with these complexities or through customizations.
Complex Manufacturing Requirements: Companies with manufacturing needs find Odoo’s MRP module insufficient.
It processes BOMs and work orders, but lacks engineering-to-order routing, scheduling optimization, and quality control workflows.
Regulatory Compliance Gaps: Regulated industries (pharmaceuticals, aerospace, financial services) may encounter gaps in compliance features.
While customization can address these, the cost and complexity exceed what teams budgeted.
The Technical Resource Dependency:
IT Requirements: Unlike SaaS solutions that handle complexity for you, Odoo demands management.
You need either IT expertise or consultant relationships—costs that aren’t obvious during evaluation.
Customization Maintenance Burden: Every customization generates debt.
Future upgrades become complex, performance optimization demands knowledge, and troubleshooting issues requires understanding both Odoo architecture and your customizations.
Support Structure Realities: Odoo’s community support covers functionality.
But when you face issues or need resolution, you rely on partner networks or expertise.
Alternative ERP Solutions Analysis
The 2025 ERP Landscape:
The ERP market has transformed.
Cloud solutions have matured, industry platforms have emerged, and the cost of ownership calculations have shifted.
Enterprise-Level Alternatives:
Oracle NetSuite: Best for: Mid-to-large businesses with complex financial requirements and global operations Strengths: Financial management, reporting and analytics, e-commerce integration Limitations: Cost ($99-999 per user/month), learning curve, customization costs heavily Migration Timeline: 3-6 months for standard implementations
SAP S/4HANA: Best for: Large enterprises with complex operations and significant IT resources Strengths: Functionality for businesses, integration capabilities, compliance features Limitations: Cost and complexity, requires expertise Consider When: Your business processes are complex for solutions
Microsoft Dynamics 365: Best for: Organizations already invested in Microsoft ecosystem Strengths: Office integration, CRM capabilities, interface for Windows users Limitations: Can become expensive with add-ons, customization complexity Consider When: You’re Microsoft-centric and need integration
Mid-Market Alternatives:
Acumatica: Best for: Growing businesses that need cloud flexibility without enterprise complexity Strengths: Pricing model, mobile capabilities, customization options Limitations: Partner network than players, learning curve for features Consider When: You need cloud architecture with room to grow
Infor CloudSuite: Best for: Industry-specific requirements with complex supply chain needs Strengths: Industry functionality, analytics, supply chain management Limitations: Can be complex to implement, industry focus may not fit all businesses Consider When: Your industry has requirements that ERPs don’t address
Small Business Alternatives:
ERPNext: Best for: Small businesses wanting open-source flexibility without Odoo’s complexity Strengths: Free and open-source, than Odoo, community support Limitations: Features, ecosystem than Odoo Consider When: You want open-source benefits but find Odoo overwhelming
Zoho ERP: Best for: Small businesses already using Zoho ecosystem Strengths: Integrated suite approach, pricing, to use Limitations: Functionality, customization constraints Consider When: You prioritize ease of use over features
Making the Switch Decision
The Decision Framework:
Current System Assessment:
- What limitations are you experiencing with your current system?
- Are these limitations to the platform or configuration issues?
- How much would it cost to resolve these limitations in your current system?
Business Requirement Analysis:
- What are your actual requirements vs. nice-to-have features?
- How standard are your business processes vs. how unique?
- What’s your timeline for implementation and return on investment?
Resource Reality Check:
- What technical expertise do you have internally?
- What’s your budget for implementation, customization, and ongoing support?
- How much disruption can your business handle during transition?
When to Select Odoo:
- Standard business processes that fit Odoo’s workflows
- Need for integrated functionality across multiple departments
- Limited budget but requirement for comprehensive ERP features
- Technical resources available for ongoing management
- Growth trajectory that may benefit from modular expansion
When to Select Alternatives:
- Complex, industry-specific requirements that demand specialized functionality
- Enterprise-scale operations with sophisticated compliance needs
- Preference for vendor-managed cloud solutions with comprehensive support
- Budget allows for premium solutions with extensive vendor support
- Critical need for proven enterprise-grade scalability and performance
Hybrid Approaches
Sometimes the best solution isn’t selecting one system.
It’s crafting an approach that harnesses the best of multiple systems while managing complexity intelligently.
Gradual Migration Strategies
The Phased Transition Approach:
Many businesses successfully migrate to Odoo by implementing it alongside existing systems, gradually transferring functions as they prove successful.
Strategy 1: Department-by-Department Migration
Phase 1: Start with CRM and Sales Implement Odoo’s CRM and sales modules while maintaining existing financial and operations systems. This approach provides immediate value while minimizing disruption.
Benefits:
- Low risk introduction to Odoo workflows
- Immediate improvement in sales process management
- You can manage user adoption gradually
- Integration with existing systems through APIs
Timeline: 2-3 months per department
Strategy 2: Function-by-Function Migration
Phase 1: Financial Management Migrate accounting and financial functions first, maintaining operations in existing systems.
Phase 2: Operations Add inventory, purchasing, and basic operations management.
Phase 3: Advanced Features Implement CRM, project management, and specialized modules.
Benefits:
- Core business functions stabilized before adding complexity
- Financial reporting consistency established early
- Operations disruption minimized
Timeline: 6-12 months total
Strategy 3: Geographic or Business Unit Migration
For multi-location businesses, implement Odoo in one location or business unit first, using lessons learned to improve implementation in subsequent locations.
Benefits:
- Proof of concept validation with real business operations
- Team expertise development before broader rollout
- Risk mitigation through limited scope pilots
Timeline: 3-6 months per location
Maintaining Legacy Systems During Transition
The Integration Bridge Strategy:
API-First Integration: Modern systems can coexist through well-designed API integrations. This allows you to maintain critical legacy functionality while gaining Odoo benefits in other areas.
Data Synchronization Approaches:
- Real-time synchronization for critical shared data (customers, inventory)
- Batch synchronization for historical and reporting data
- Manual synchronization for exceptional transactions
Common Integration Patterns:
Pattern 1: Odoo as Front-End, Legacy as Back-End Use Odoo for user-facing functions (CRM, project management) while maintaining complex backend processes in legacy systems.
Example: Manufacturing company using Odoo for sales and customer service while maintaining complex production planning in specialized manufacturing software.
Pattern 2: Legacy as Front-End, Odoo as Back-End Maintain familiar user interfaces while leveraging Odoo’s integration and reporting capabilities.
Example: Service company maintaining custom client portal while using Odoo for internal operations and financial management.
Pattern 3: Best-of-Breed Integration Use each system for its strengths while maintaining data consistency through integration.
Example: E-commerce company using Shopify for online sales, Odoo for operations and accounting, and specialized shipping software for logistics.
Integration Success Factors:
Data Governance:
- Clear ownership of master data (customers, products, pricing)
- Defined synchronization schedules and conflict resolution procedures
- Monitoring and alerting for integration failures
Change Management:
- User training on multi-system workflows
- Clear procedures for data entry and modification
- Support processes that understand integrated system dependencies
Technical Architecture:
- Robust error handling and retry mechanisms
- Monitoring and logging for integration health
- Backup and recovery procedures that account for system dependencies
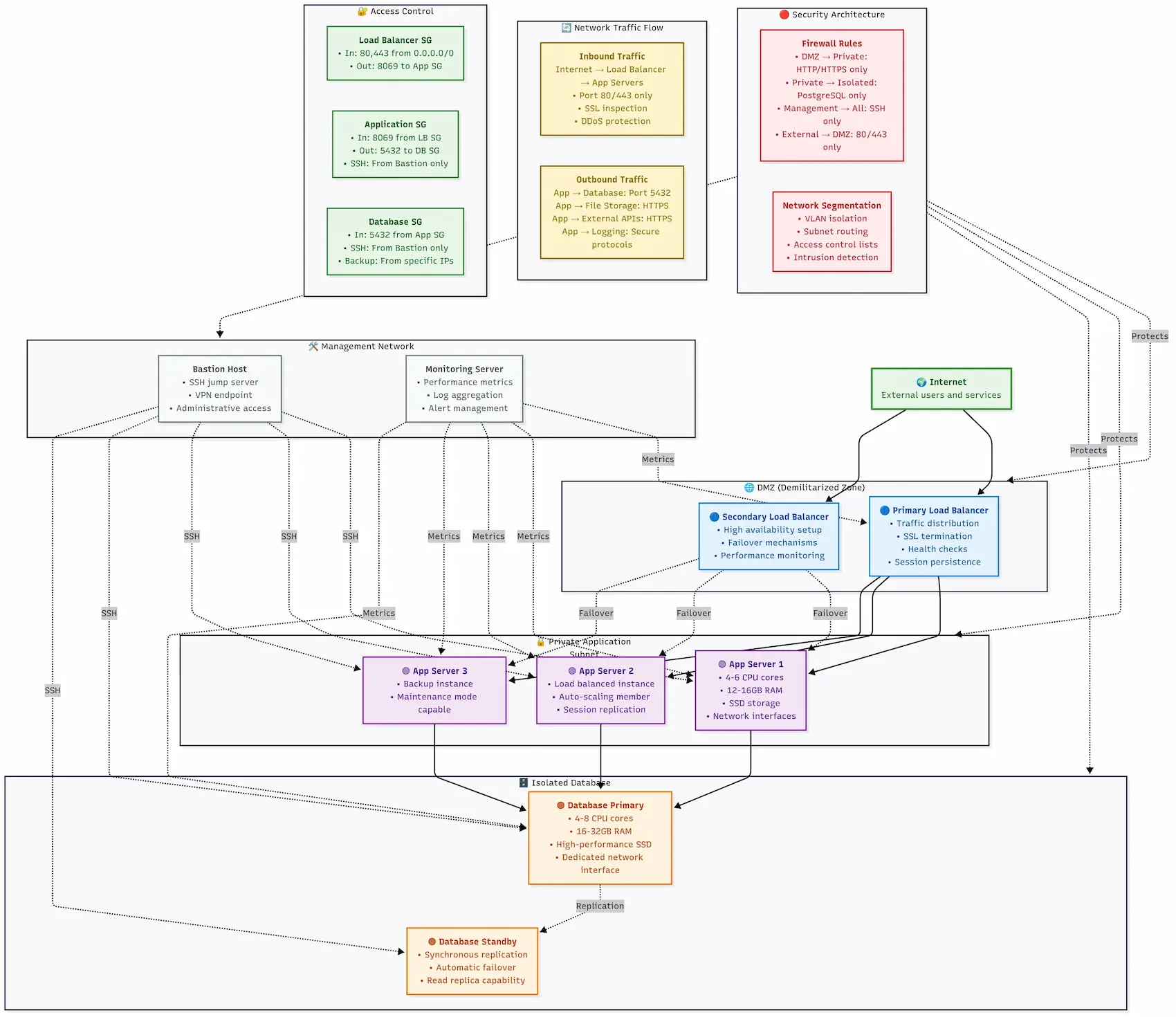 Production network architecture demonstrating secure integration patterns between Odoo and existing legacy systems
Production network architecture demonstrating secure integration patterns between Odoo and existing legacy systems
Alternative Solution Decision Matrix:
📋 Download Odoo Decision Matrix Framework - Complete evaluation framework to assess whether Odoo is right for your business situation
Migration Readiness Checklist:
Before committing to any solution, ensure current system limitations are documented, business requirements are validated, technical resources are assessed, and total cost of ownership is calculated for a 3-5 year timeline.
Remember: the best ERP is the one that fits your business reality, not the one that looks best in demos. Sometimes that’s Odoo, sometimes it’s not. The key is making an informed decision based on honest assessment of your needs, capabilities, and constraints.
Creative Surprise: The Odoo Implementation Readiness Assessment
Here’s where things get really interesting. Research across dozens of Odoo implementations reveals a clear pattern: the companies that succeed aren’t necessarily the ones with the biggest budgets or the best technical teams. They’re the ones who honestly assessed their readiness before diving in.
Most implementation guides skip this crucial step. They assume you’re ready just because you’ve decided to implement. That’s like assuming you’re ready to run a marathon just because you bought running shoes.
Based on this research, three comprehensive assessment tools have been developed that will tell you exactly where you stand and what you need to work on before starting your implementation. Think of these as your pre-flight checklist for Odoo success.
The Triple Assessment Framework
Assessment #1: The Complete Readiness Scorecard
This isn’t your typical “rate yourself 1-10” questionnaire. It’s a brutally honest 300-point assessment that evaluates four critical dimensions:
- Organizational Readiness (100 points): Leadership commitment, change management capability, resource allocation, and timeline realism
- Business Process Readiness (75 points): Process documentation, requirements clarity, and willingness to adapt
- Technical Readiness (75 points): Infrastructure capability, data quality, and technical expertise
- Financial & Resource Readiness (50 points): Budget planning and partner strategy
Download: Complete Implementation Readiness Checklist
Case studies show companies scoring 280+ still struggling because they ignored the few areas where they scored low.
Conversely, analysis reveals companies scoring 220 succeeding brilliantly because they addressed their weak spots first.
Assessment #2: Technical Infrastructure Scorecard
This 200-point deep-dive focuses specifically on your technical foundation:
- Server Infrastructure (50 points): Hardware specs, hosting environment, and scalability planning
- Database & Storage (40 points): PostgreSQL readiness, backup procedures, and data management
- Network & Security (35 points): Connectivity, access controls, and security frameworks
- Integration & APIs (30 points): External system integration capability and third-party services
- Technical Expertise (45 points): Internal capabilities and development skills
Download: Technical Readiness Scorecard
Case studies document manufacturing companies scoring perfectly on everything except database administration (scoring 15 out of 30).
Analysis shows that delaying implementation by six weeks to train IT teams and bring in PostgreSQL consultants saves months of performance issues later.
🎯 Start with the Foundation Assessment
Assessment #2 mentions "Server Infrastructure (50 points)" and "Technical Expertise (45 points)"—but here's the reality: your hosting model choice IS your technical readiness test. Before spending 2-3 hours on detailed scorecards, invest 2 minutes answering the fundamental question: does your team have the capacity for self-hosting?
Our Hosting Advisor is the fastest readiness assessment you can take. It evaluates your IT staffing (do you have dedicated Linux admins?), available budget (including opportunity costs), and growth trajectory—then tells you if self-hosting is realistic or if you're setting yourself up for the 73% who fail due to inadequate technical foundation. Think of it as Assessment #0: the prerequisite.
Assessment #3: The 30-60-90 Day Success Plan
This is the secret sauce that separates successful implementations from expensive disasters.
Most companies focus all their energy on getting to go-live, then completely wing it afterward.
That’s backwards.
The real work begins after go-live.
This detailed plan maps out exactly what you need to do in your first 90 days to achieve:
- 30 Days: System stabilization and immediate issue resolution
- 60 Days: Process optimization and advanced feature adoption
- 90 Days: Performance excellence and continuous improvement framework
Download: 30-60-90 Day Success Plan
Each assessment comes with detailed scoring guides, risk mitigation strategies, and specific action items for improvement.
I didn’t just create questionnaires—I built complete roadmaps for success.
How to Use These Assessments
Step 1: Take All Three Assessments Honestly
Set aside 2-3 hours and work through each assessment with your core team. Don’t try to make yourselves look good—brutal honesty is what will save you later.
Step 2: Identify Your Readiness Level
- Green Light: High scores across all assessments? You’re ready to start implementation planning
- Yellow Light: Strong in most areas with some gaps? Address the gaps first, then proceed
- Red Light: Multiple low scores or critical gaps? Delay implementation until you’re truly ready
Step 3: Create Your Improvement Plan
Each assessment includes specific recommendations for different scoring ranges. Use these to create a detailed improvement plan before starting your implementation.
Step 4: Re-assess Before Starting
Once you’ve worked on your improvement areas, retake the assessments. Only proceed when you’re genuinely ready, not when your arbitrary timeline says you should start.
Your Implementation Action Plan
You now control the same frameworks and assessments that prevent the 73% failure rate in DIY Odoo implementations. The TCO calculators, partner evaluation matrices, and 30-60-90 day plans in this guide eliminate the planning mistakes that cost businesses $50K-$200K in failed implementations.
Three implementation truths:
- Failure is predictable, not random—companies that skip readiness assessments fail at 3x the rate of those who complete them
- Go-live is the beginning, not the end—90% of user adoption happens in the first 90 days post-deployment
- DIY doesn’t mean alone—strategic use of consultants for 20% of tasks saves 60% of total costs
Your next 7 days:
⏱️ Start with the 2-minute decision that affects everything else: Before diving into readiness assessments, TCO calculators, and risk phase identification—get your hosting model right. Every framework in this guide (budget planning, partner selection, technical architecture) depends on whether you’re self-hosting or using managed services. Our Hosting Advisor gives you a data-driven answer based on your team’s actual capacity and constraints. Think of it as step zero of your action plan—the foundation decision that makes all subsequent planning accurate. Get your hosting recommendation now →
- Complete the readiness assessment with your core team (be brutally honest about gaps)
- Run the TCO calculator with your actual modules and user count (not the demo configuration)
- Identify your highest-risk phase (data migration? user training? module configuration?)
Implementation success isn’t luck—it’s preparation. Execute with discipline. 🚀
Last updated: September 2025 | Found this guide valuable? Share it with another business owner planning an Odoo implementation.
Skip Hours of Configuration Debugging
Generic Odoo installations aren't production-ready. The Config Pack provides battle-tested configurations for NGINX, PostgreSQL, and Odoo - optimized for security, performance, and reliability.
What You Get
- 5 Production Configs:
- ✓ NGINX reverse proxy (SSL, caching, load balancing)
- ✓ PostgreSQL tuning (optimized for Odoo workloads)
- ✓ Odoo production settings (security hardened)
- ✓ Systemd service files (auto-restart, logging)
- ✓ Firewall rules (UFW/iptables security lockdown)
Investment: $17 one-time payment
What you avoid: Hours of debugging, trial-and-error, and expensive consultants
Guarantee: 30-day money-back guarantee. No questions asked.
Get Production Config Pack $17 →